Structural basis for regulation of Arp2/3 complex by GMF.
Luan, Q., Nolen, B.J.(2013) Nat Struct Mol Biol 20: 1062-1068
- PubMed: 23893131
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2628
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JD2 - PubMed Abstract:
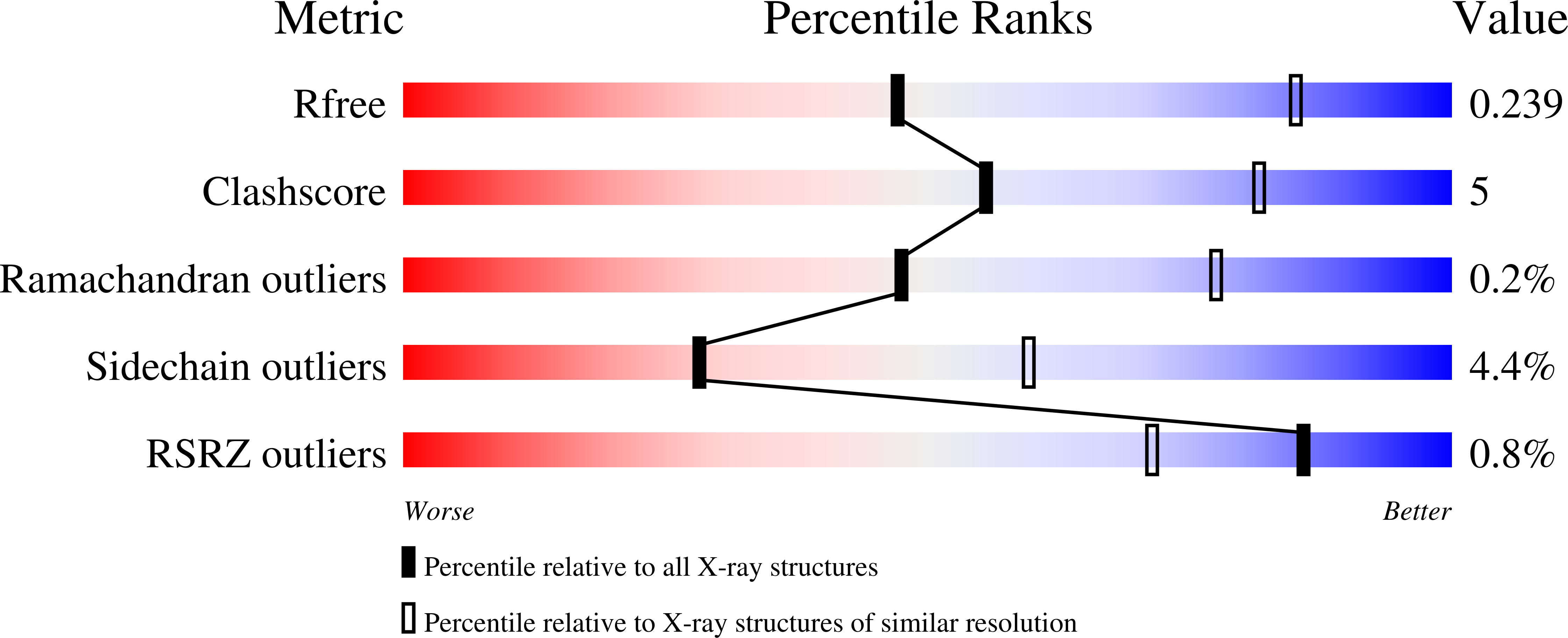
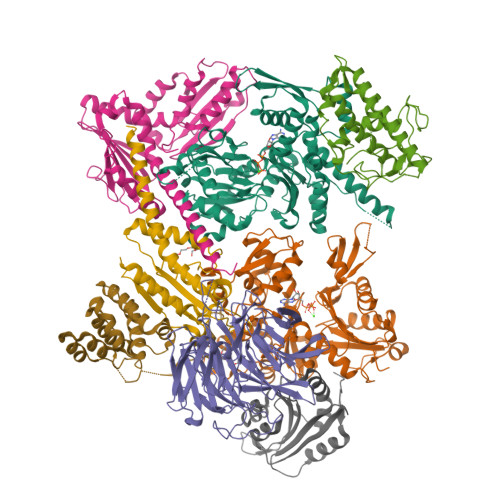
The Arp2/3 complex mediates formation of complex cellular structures such as lamellipodia by nucleating branched actin filaments. Arp2/3-complex activity is precisely controlled by over a dozen regulators, yet the structural mechanism by which regulators interact with the complex is unknown. GMF is a recently discovered regulator of the Arp2/3 complex that can inhibit nucleation and disassemble branches. We solved the structure of the 240-kDa assembly of Mus musculus GMF and Bos taurus Arp2/3 complex and found that GMF binds the barbed end of Arp2, overlapping with the proposed binding site of WASP-family proteins. The structure suggests that GMF can bind branch junctions in the manner that cofilin binds filament sides, consistent with a modified cofilin-like mechanism for debranching by GMF. The GMF-Arp2 interface reveals how the ADF-H actin-binding domain in GMF is exploited to specifically recognize Arp2/3 complex and not actin.
Organizational Affiliation:
1] Institute of Molecular Biology, University of Oregon, Eugene, Oregon, USA. [2] Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Oregon, Eugene, Oregon, USA.