Structural basis of substrate specificity and protease inhibition in norwalk virus.
Muhaxhiri, Z., Deng, L., Shanker, S., Sankaran, B., Estes, M.K., Palzkill, T., Song, Y., Prasad, B.V.(2013) J Virol 87: 4281-4292
- PubMed: 23365454
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02869-12
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4IMQ, 4IMZ, 4IN1, 4IN2, 4INH - PubMed Abstract:
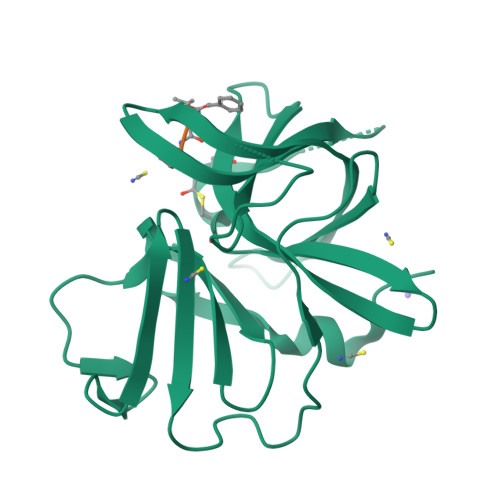
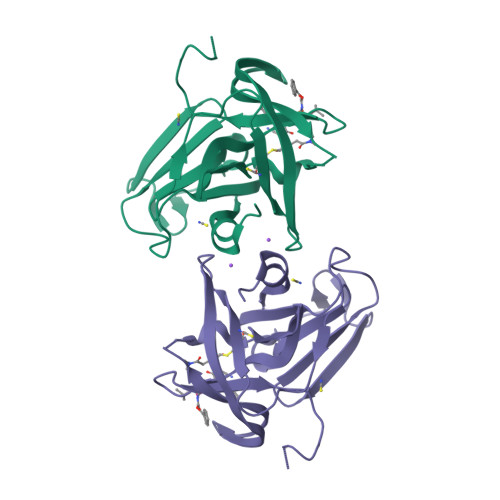
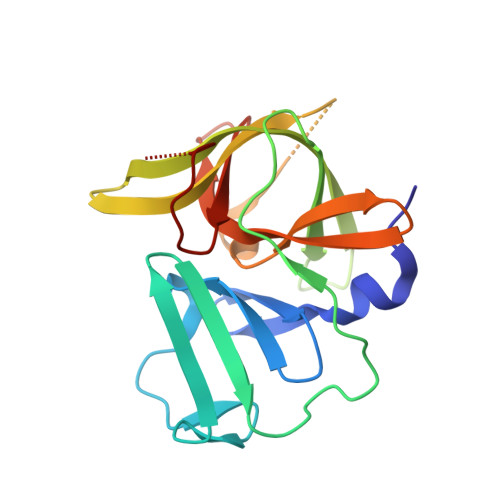
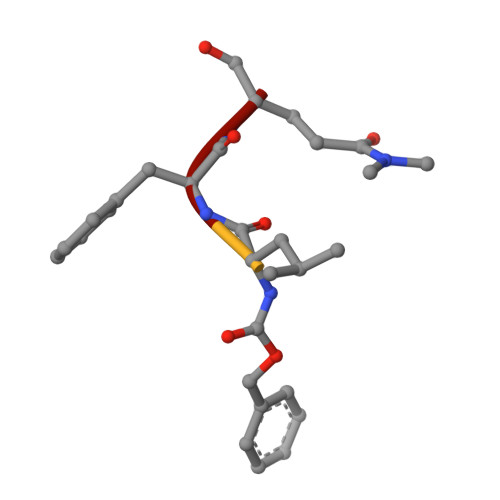
Norwalk virus (NV), the prototype human calicivirus, is the leading cause of nonbacterial acute gastroenteritis. The NV protease cleaves the polyprotein encoded by open reading frame 1 of the viral genome at five nonhomologous sites, releasing six nonstructural proteins that are essential for viral replication. The structural details of how NV protease recognizes multiple substrates are unclear. In our X-ray structure of an NV protease construct, we observed that the C-terminal tail, representing the native substrate positions P5 to P1, is inserted into the active site cleft of the neighboring protease molecule, providing atomic details of how NV protease recognizes a substrate. The crystallographic structure of NV protease with the C-terminal tail redesigned to mimic P4 to P1 of another substrate site provided further structural details on how the active site accommodates sequence variations in the substrates. Based on these structural analyses, substrate-based aldehyde inhibitors were synthesized and screened for inhibition potency. Crystallographic structures of the protease in complex with each of the three most potent inhibitors were determined. These structures showed concerted conformational changes in the S4 and S2 pockets of the protease to accommodate variations in the P4 and P2 residues of the substrate/inhibitor, which could be a mechanism for how the NV protease recognizes multiple sites in the polyprotein with differential affinities during virus replication. These structures further indicate that the mechanism of inhibition by these inhibitors involves covalent bond formation with the side chain of the conserved cysteine in the active site by nucleophilic addition, and such substrate-based aldehydes could be effective protease inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Verna and Marrs McLean Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, USA.