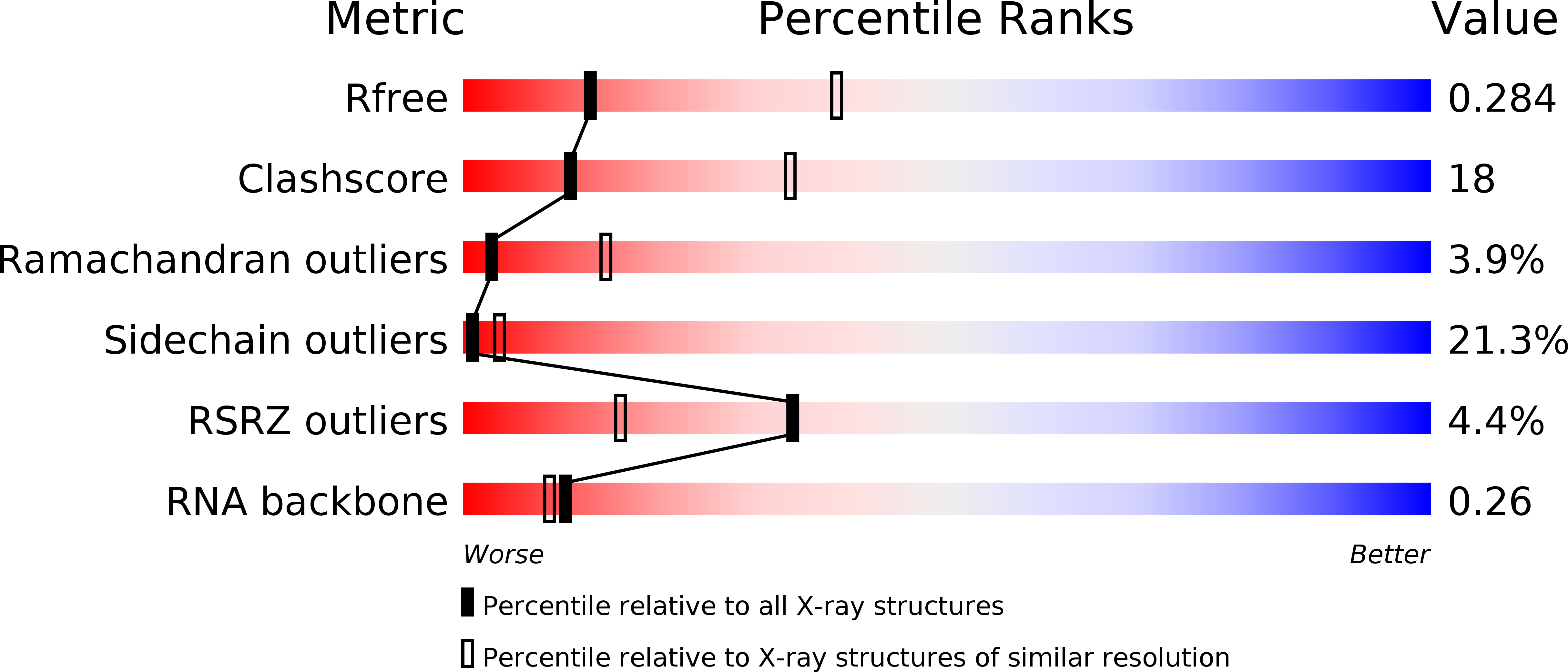
Recognition and cleavage of a nonstructured CRISPR RNA by its processing endoribonuclease Cas6.
Shao, Y., Li, H.(2013) Structure 21: 385-393
- PubMed: 23454186
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2013.01.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4ILL, 4ILM, 4ILR - PubMed Abstract:
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPRs) confer adaptive immunity to prokaryotes through a small RNA-mediated mechanism. Specific endoribonucleases are required by all CRISPR-bearing organisms to process CRISPR RNAs into small RNA that serve as guides for defensive effector complexes. The molecular mechanism of how the endoribonucleases process the class of CRISPR RNA containing no predicted secondary structural features remains largely elusive. Here, we report cocrystal structures of a processing endoribonuclease bound with a noncleavable RNA substrate and its product-like fragment derived from a nonpalindramic repeat. The enzyme stabilizes a short RNA stem-loop structure near the cleavage site and cleaves the phosphodiester bond using an active site comprised of arginine and lysine residues. The distinct RNA binding and cleavage mechanisms underline the diversity in CRISPR RNA processing.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Molecular Biophysics, Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL 32306, USA