The c-di-GMP recognition mechanism of the PilZ domain of bacterial cellulose synthase subunit A
Fujiwara, T., Komoda, K., Sakurai, N., Tajima, K., Tanaka, I., Yao, M.(2013) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 431: 802-807
- PubMed: 23291177
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.103
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4I86 - PubMed Abstract:
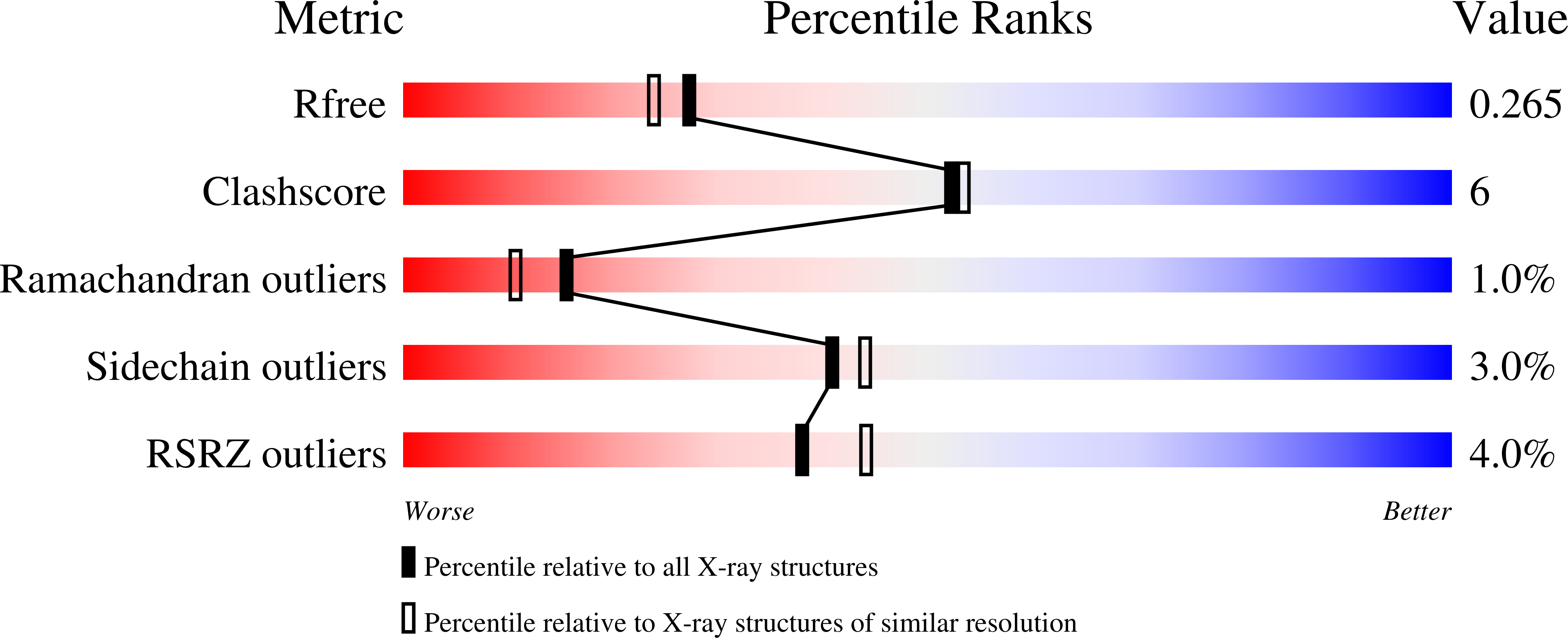
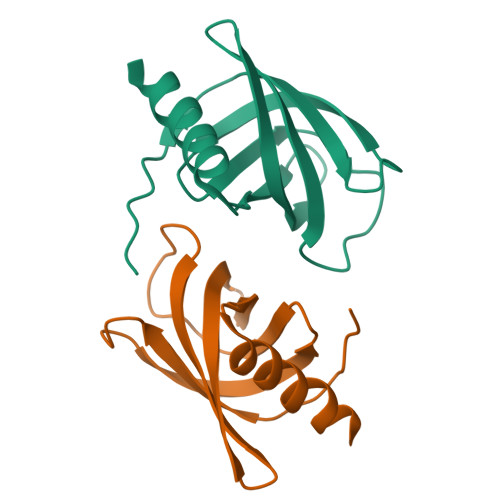
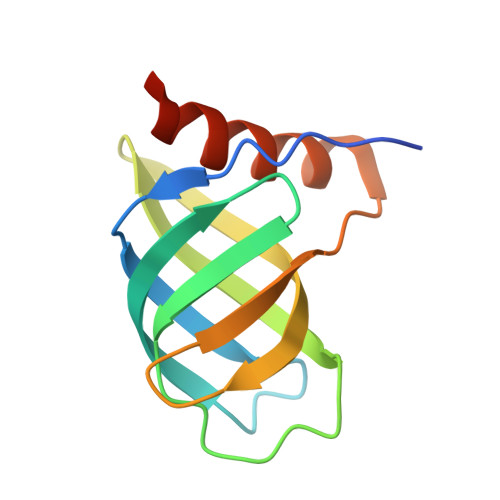
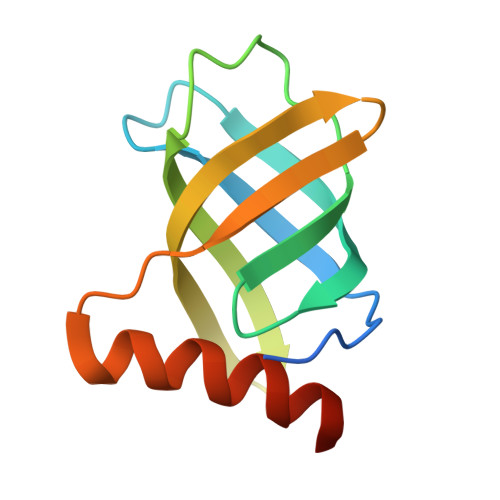
In some Proteobacteria and Firmicutes such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio cholerae, Xanthomonas campestris, and Clostridium difficile, cyclic dimeric guanosine monophosphate (c-di-GMP) is known to regulate cellular processes, including motility, biofilm formation, and virulence, as a second messenger. Cellulose production in Acetobacter xylinum, a model organism of cellulose biosynthesis, also depends on by cellular c-di-GMP level. In cellulose-synthesizing bacteria, a terminal complex localized in the cell membrane synthesizes cellulose and regulates the production of cellulose sensed by c-di-GMP. Although previous studies indicated that the PilZ domain conserved in cellulose synthase subunit A (CeSA) was part of a receptor for c-di-GMP, the recognition mechanism by PilZ domain of CeSA remains unclear. In the present study, we studied the interaction between c-di-GMP and the PilZ domain of CeSA from a structural viewpoint. First, we solved the crystal structure of the PilZ domain of CeSA from A. xylinum (AxCeSA-PilZ) at 2.1Å resolution. Then, comparison of the sequence and structure of AxCeSA-PilZ to those of known structures of PilZ, such as VCA0042, PP4397, and PA4608, indicated the involvement of Lys573 and Arg643 of AxCeSA-PilZ in the recognition of c-di-GMP besides the RxxxR motif. Finally, the binding characteristics of c-di-GMP to AxCeSA-PilZ and mutants were determined with isothermal titration calorimetry, indicating that the residues corresponding to Lys573 and Arg643 in AxCeSA-PilZ generally contribute to the binding of c-di-GMP to PilZ.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Life Science, Hokkaido University, Kita-10, Nishi-8, Kita-ku, Sapporo 060-0810, Japan.