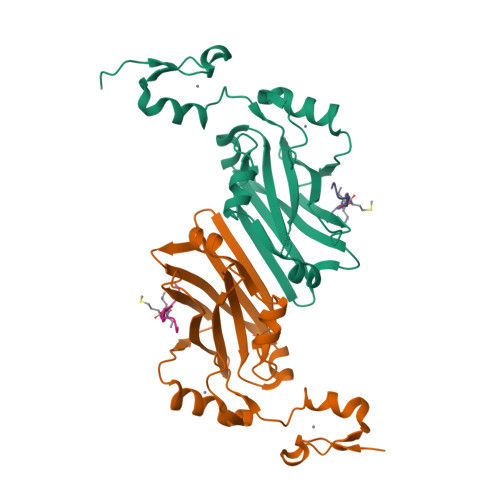
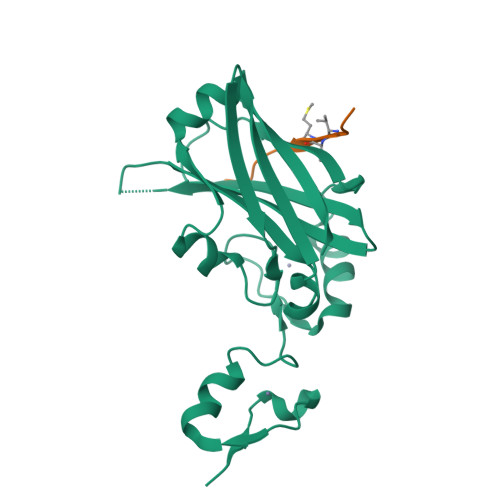
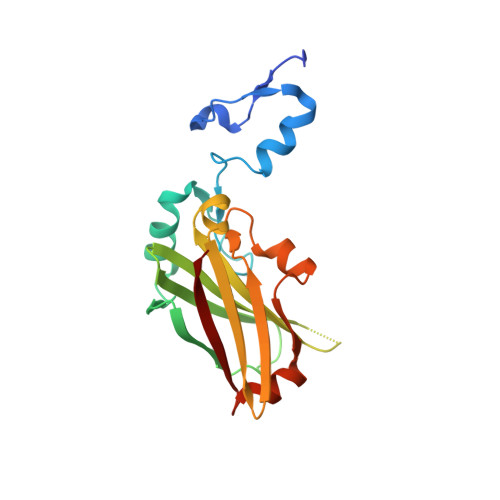
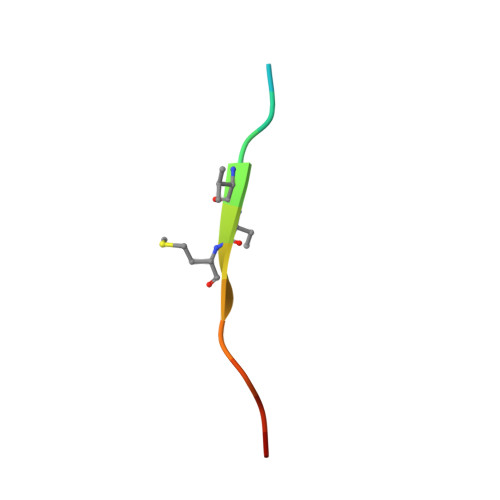
Structure-based design of covalent siah inhibitors.
Stebbins, J.L., Santelli, E., Feng, Y., De, S.K., Purves, A., Motamedchaboki, K., Wu, B., Ronai, Z.A., Liddington, R.C., Pellecchia, M.(2013) Chem Biol 20: 973-982
- PubMed: 23891150
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.06.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4I7B, 4I7C, 4I7D - PubMed Abstract:
The E3 ubiquitin ligase Siah regulates key cellular events that are central to cancer development and progression. A promising route to Siah inhibition is disrupting its interactions with adaptor proteins. However, typical of protein-protein interactions, traditional unbiased approaches to ligand discovery did not produce viable hits against this target, despite considerable effort and a multitude of approaches. Ultimately, a rational structure-based design strategy was successful for the identification of Siah inhibitors in which peptide binding drives specific covalent bond formation with the target. X-ray crystallography, mass spectrometry, and functional data demonstrate that these peptide mimetics are efficient covalent inhibitors of Siah and antagonize Siah-dependent regulation of Erk and Hif signaling in the cell. The proposed strategy may result useful as a general approach to the design of peptide-based inhibitors of other protein-protein interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Signal Transduction Program and Cell Death Program, Cancer Center, Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute, 10901 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.