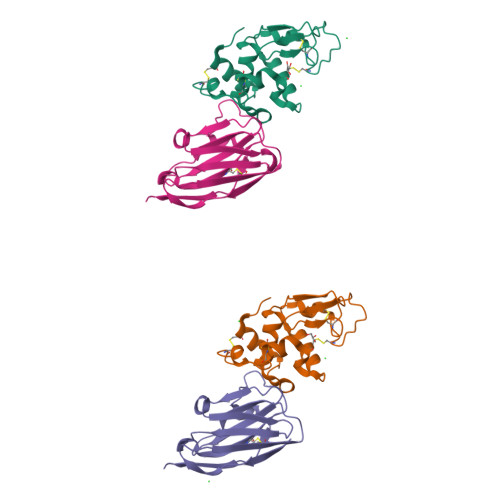
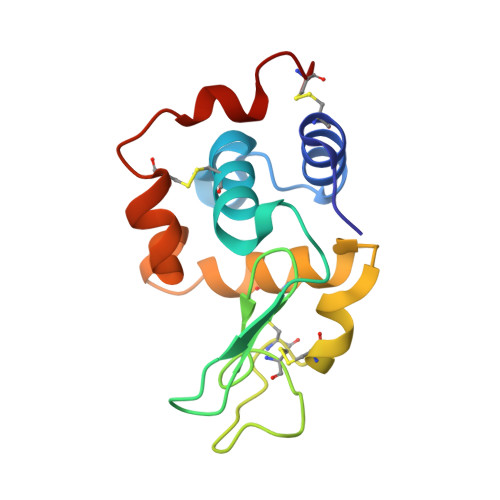
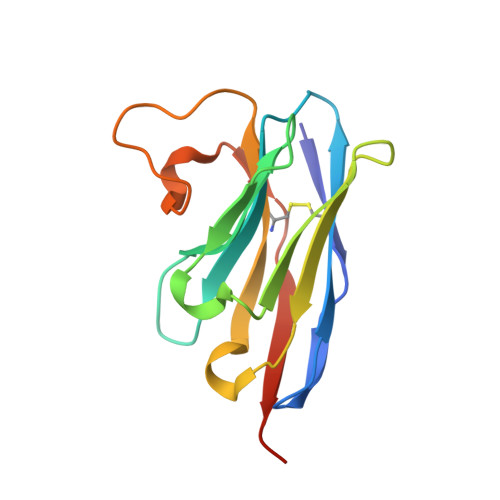
A nanobody binding to non-amyloidogenic regions of the protein human lysozyme enhances partial unfolding but inhibits amyloid fibril formation.
De Genst, E., Chan, P.H., Pardon, E., Hsu, S.T., Kumita, J.R., Christodoulou, J., Menzer, L., Chirgadze, D.Y., Robinson, C.V., Muyldermans, S., Matagne, A., Wyns, L., Dobson, C.M., Dumoulin, M.(2013) J Phys Chem B 117: 13245-13258
- PubMed: 23919586
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp403425z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4I0C - PubMed Abstract:
We report the effects of the interaction of two camelid antibody fragments, generally called nanobodies, namely cAb-HuL5 and a stabilized and more aggregation-resistant variant cAb-HuL5G obtained by protein engineering, on the properties of two amyloidogenic variants of human lysozyme, I56T and D67H, whose deposition in vital organs including the liver, kidney, and spleen is associated with a familial non-neuropathic systemic amyloidosis. Both NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallographic studies reveal that cAb-HuL5 binds to the α-domain, one of the two lobes of the native lysozyme structure. The binding of cAb-HuL5/cAb-HuL5G strongly inhibits fibril formation by the amyloidogenic variants; it does not, however, suppress the locally transient cooperative unfolding transitions, characteristic of these variants, in which the β-domain and the C-helix unfold and which represents key early intermediate species in the formation of amyloid fibrils. Therefore, unlike two other nanobodies previously described, cAb-HuL5/cAb-HuL5G does not inhibit fibril formation via the restoration of the global cooperativity of the native structure of the lysozyme variants to that characteristic of the wild-type protein. Instead, it inhibits a subsequent step in the assembly of the fibrils, involving the unfolding and structural reorganization of the α-domain. These results show that nanobodies can protect against the formation of pathogenic aggregates at different stages in the structural transition of a protein from the soluble native state into amyloid fibrils, illustrating their value as structural probes to study the molecular mechanisms of amyloid fibril formation. Combined with their amenability to protein engineering techniques to improve their stability and solubility, these findings support the suggestion that nanobodies can potentially be developed as therapeutics to combat protein misfolding diseases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge, Lensfield Road, Cambridge CB2 1EW, U.K.