Functional and structural analysis of the human SLO3 pH- and voltage-gated K+ channel.
Leonetti, M.D., Yuan, P., Hsiung, Y., Mackinnon, R.(2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 19274-19279
- PubMed: 23129643
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1215078109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4HPF - PubMed Abstract:
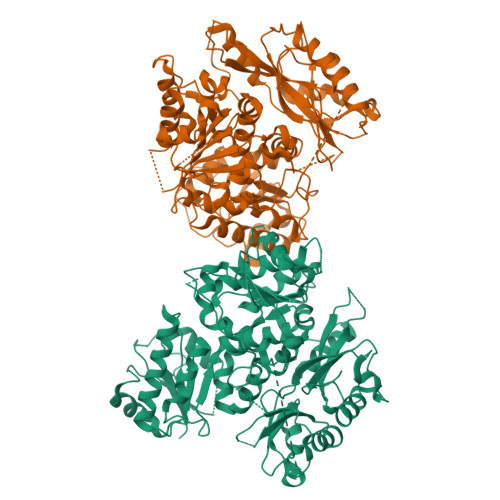
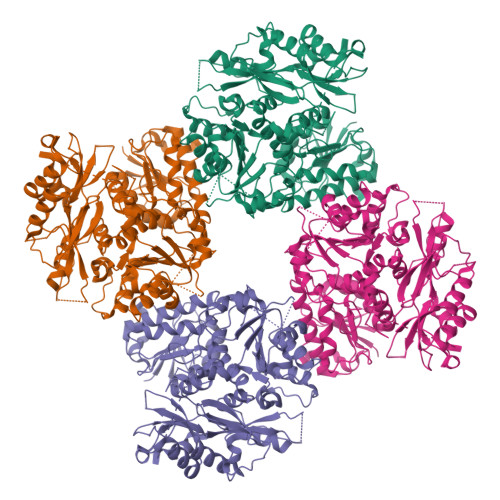
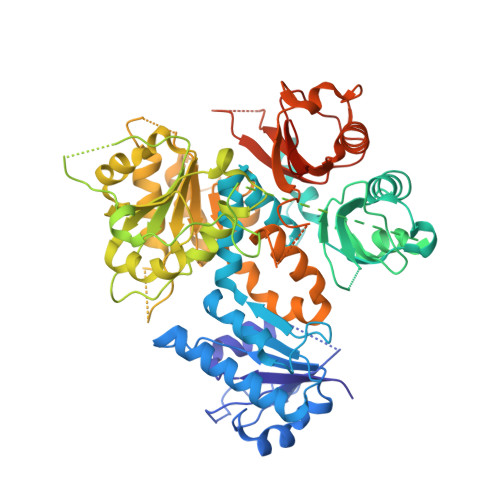
The activation of eukaryotic SLO K(+) channels by intracellular cues, mediated by a cytoplasmic structure called the gating ring, is central to their physiological roles. SLO3 channels are exclusively expressed in mammalian sperm, where variations of intracellular pH are critical to cellular function. Previous studies primarily focused on the mouse SLO3 orthologue and revealed that, in murine sperm, SLO3 mediates a voltage- and alkalization-activated K(+) current essential to male fertility. Here we investigate the activation of the human SLO3 channel by intracellular pH at the functional and structural level. By using electrophysiology in a heterologous system, we show that human SLO3 opens upon intracellular pH increase and that its expression and functional properties are modulated by LRRC52, a testis-specific accessory subunit. We next present the crystal structure of the human SLO3 gating ring. Comparison with the known structures of the corresponding domain from SLO1, a Ca(2+)-activated homologue, suggests that the SLO3 gating ring structure may represent an open state. Together, these results present insights into the function of a protein expected to be critical for human reproduction and provide a framework to study the mechanism of pH gating in SLO3 channels.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Molecular Neurobiology and Biophysics and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, The Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10065, USA.