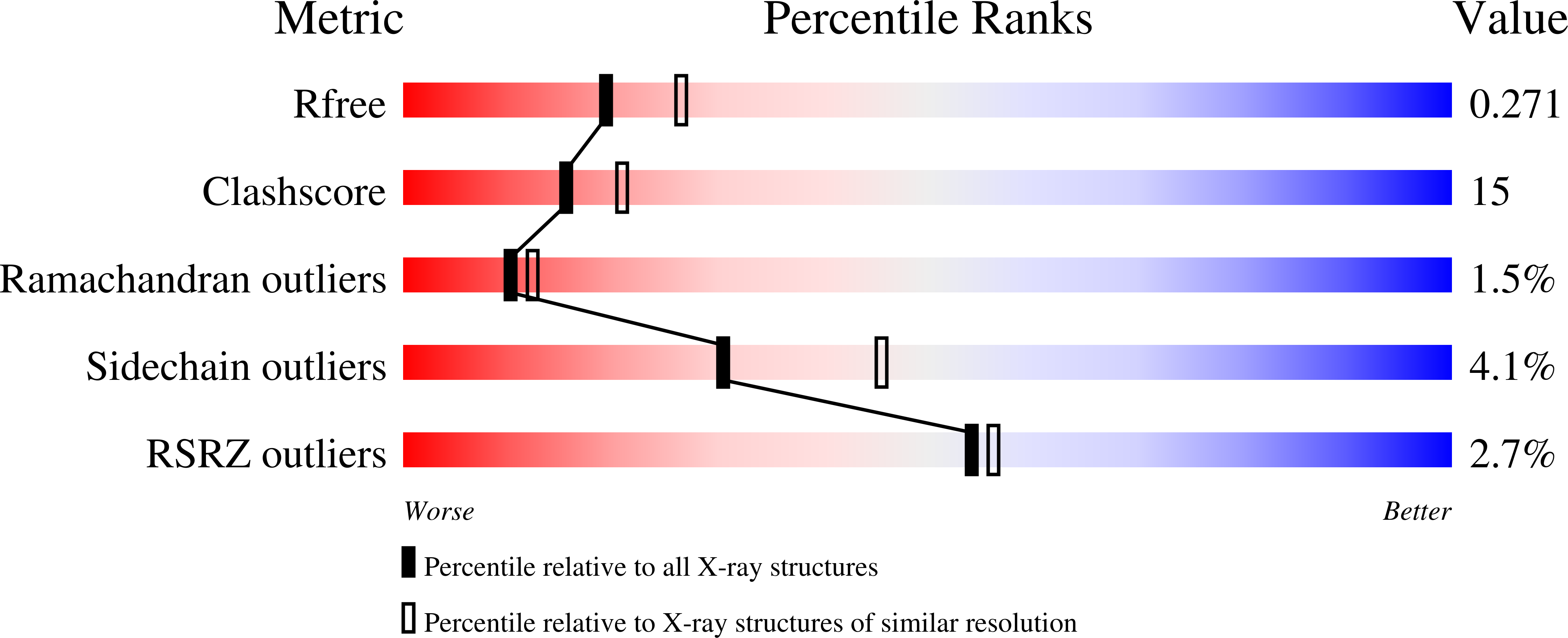
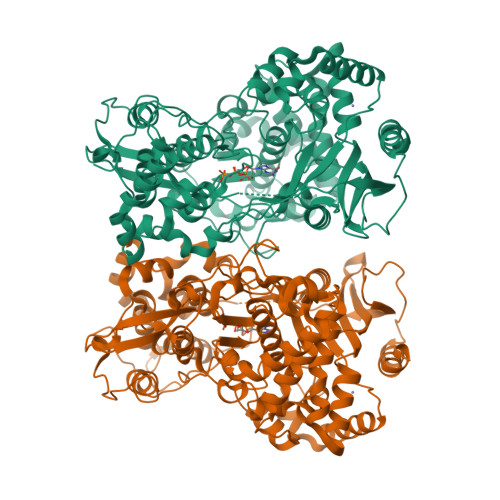
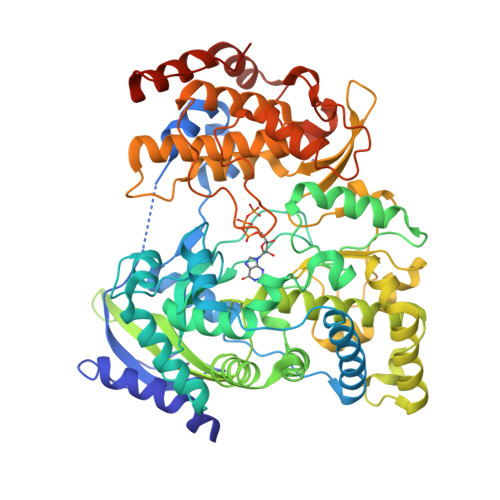
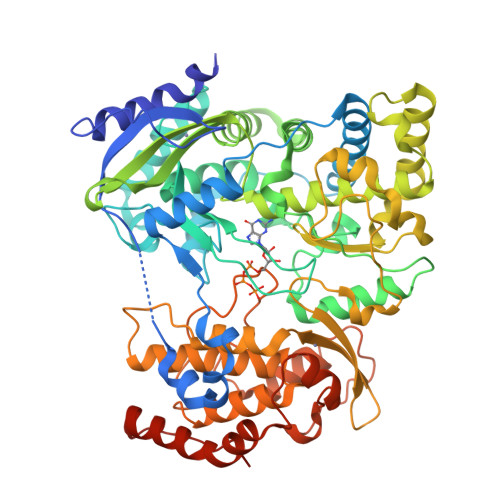
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Japanese encephalitis virus binds the initiator nucleotide GTP to form a mechanistically important pre-initiation state.
Surana, P., Satchidanandam, V., Nair, D.T.(2014) Nucleic Acids Res 42: 2758-2773
- PubMed: 24293643
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1106
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4HDG, 4HDH, 4MTP - PubMed Abstract:
Flaviviral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps) initiate replication of the single-stranded RNA genome in the absence of a primer. The template sequence 5'-CU-3' at the 3'-end of the flaviviral genome is highly conserved. Surprisingly, flaviviral RdRps require high concentrations of the second incoming nucleotide GTP to catalyze de novo template-dependent RNA synthesis. We show that GTP stimulates de novo RNA synthesis by RdRp from Japanese encephalitis virus (jRdRp) also. Crystal structures of jRdRp complexed with GTP and ATP provide a basis for specific recognition of GTP. Comparison of the jRdRpGTP structure with other viral RdRp-GTP structures shows that GTP binds jRdRp in a novel conformation. Apo-jRdRp structure suggests that the conserved motif F of jRdRp occupies multiple conformations in absence of GTP. Motif F becomes ordered on GTP binding and occludes the nucleotide triphosphate entry tunnel. Mutational analysis of key residues that interact with GTP evinces that the jRdRpGTP structure represents a novel pre-initiation state. Also, binding studies show that GTP binding reduces affinity of RdRp for RNA, but the presence of the catalytic Mn(2+) ion abolishes this inhibition. Collectively, these observations suggest that the observed pre-initiation state may serve as a checkpoint to prevent erroneous template-independent RNA synthesis by jRdRp during initiation.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS-TIFR), UAS-GKVK Campus, Bellary Road, Bangalore 560065, India and Department of Microbiology and Cell biology, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012, India.