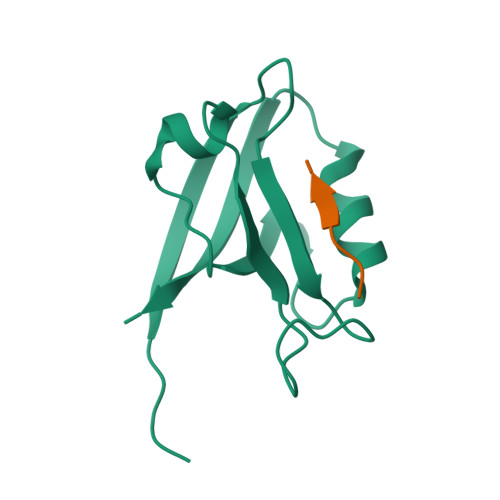
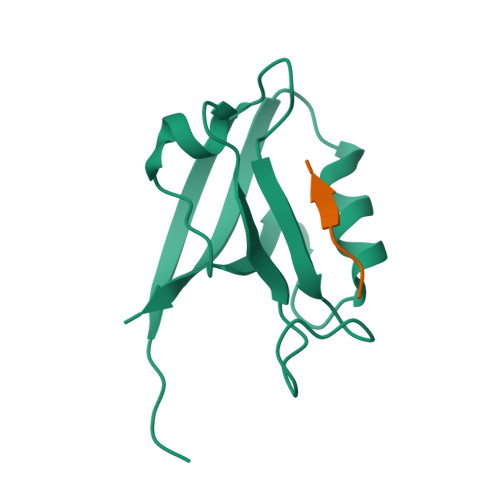
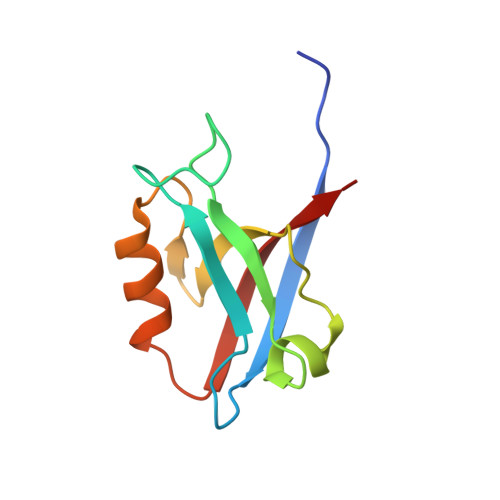
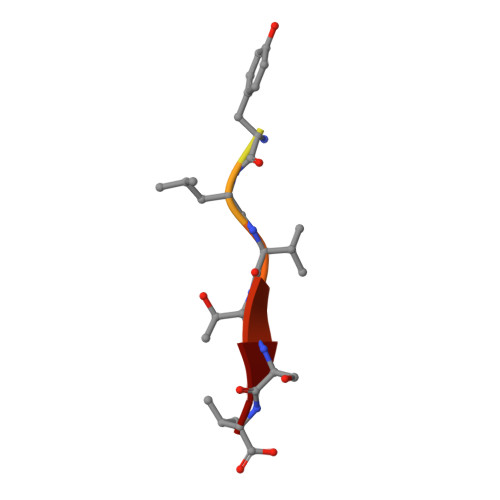
Structure of the Human Discs Large 1 PDZ2- Adenomatous Polyposis Coli Cytoskeletal Polarity Complex: Insight into Peptide Engagement and PDZ Clustering.
Slep, K.C.(2012) PLoS One 7: e50097-e50097
- PubMed: 23185543
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050097
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4G69 - PubMed Abstract:
The membrane associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family member, human Discs Large 1 (hDlg1) uses a PDZ domain array to interact with the polarity determinant, the Adenomatous Polyposis Coli (APC) microtubule plus end binding protein. The hDLG1-APC complex mediates a dynamic attachment between microtubule plus ends and polarized cortical determinants in epithelial cells, stem cells, and neuronal synapses. Using its multi-domain architecture, hDlg1 both scaffolds and regulates the polarity factors it engages. Molecular details underlying the hDlg1-APC interaction and insight into how the hDlg1 PDZ array may cluster and regulate its binding factors remain to be determined. Here, I present the crystal structure of the hDlg1 PDZ2-APC complex and the molecular determinants that mediate APC binding. The hDlg1 PDZ2-APC complex also provides insight into potential modes of ligand-dependent PDZ domain clustering that may parallel Dlg scaffold regulatory mechanisms. The hDlg1 PDZ2-APC complex presented here represents a core biological complex that bridges polarized cortical determinants with the dynamic microtubule cytoskeleton.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, United States of America. kslep@bio.unc.edu