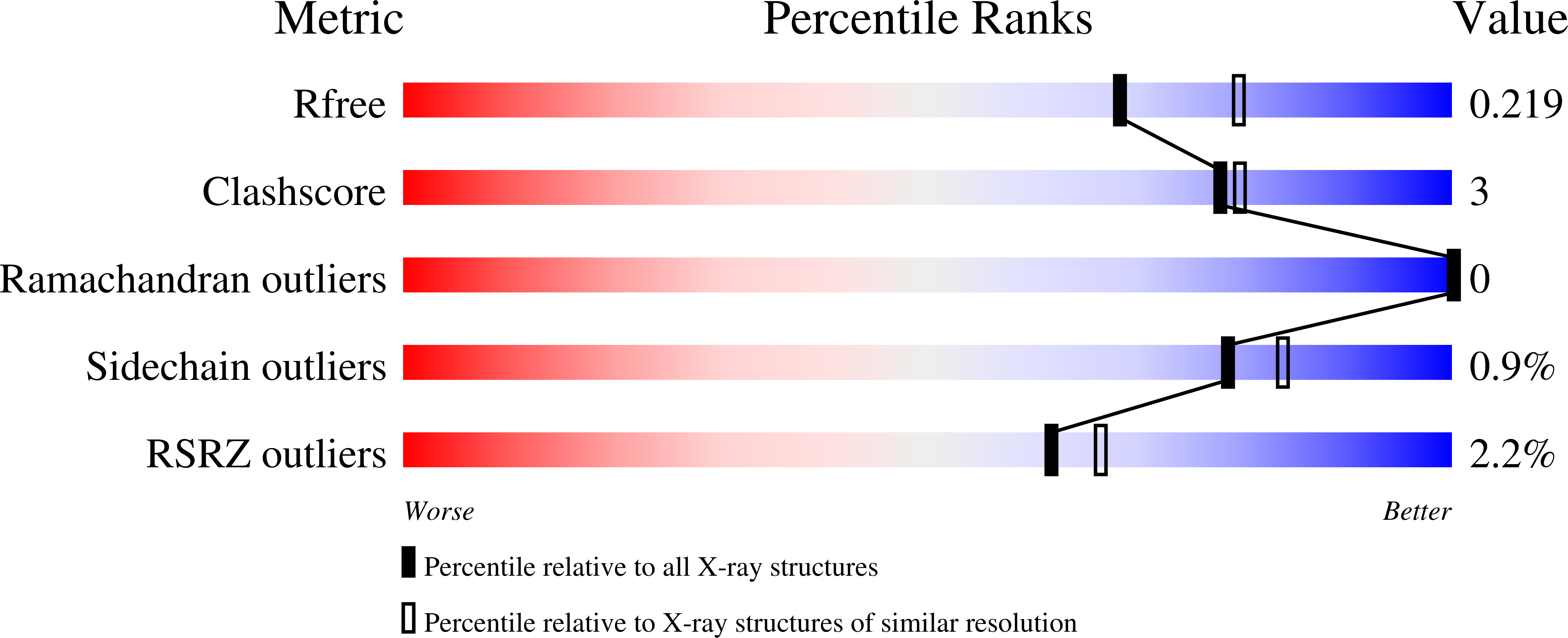
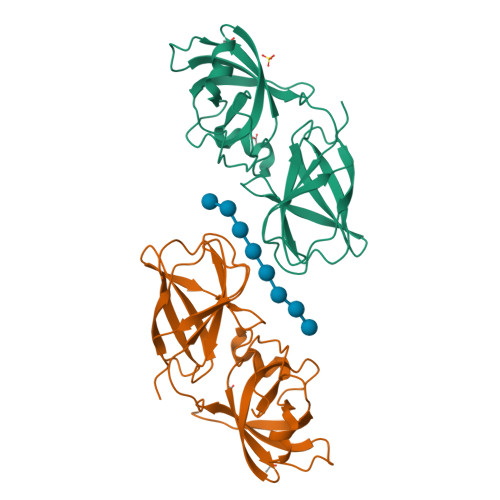
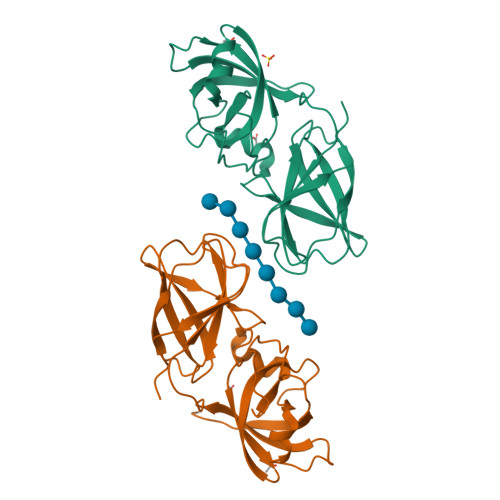
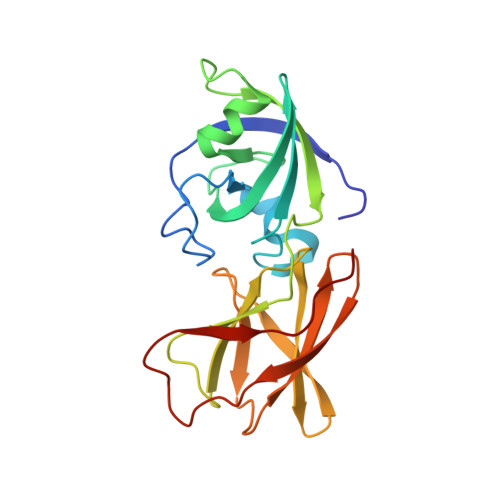
Structural basis for entropy-driven cellulose binding by a type-A cellulose-binding module (CBM) and bacterial expansin.
Georgelis, N., Yennawar, N.H., Cosgrove, D.J.(2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 14830-14835
- PubMed: 22927418
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1213200109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4FER, 4FFT, 4FG2, 4FG4 - PubMed Abstract:
Components of modular cellulases, type-A cellulose-binding modules (CBMs) bind to crystalline cellulose and enhance enzyme effectiveness, but structural details of the interaction are uncertain. We analyzed cellulose binding by EXLX1, a bacterial expansin with ability to loosen plant cell walls and whose domain D2 has type-A CBM characteristics. EXLX1 strongly binds to crystalline cellulose via D2, whereas its affinity for soluble cellooligosaccharides is weak. Calorimetry indicated cellulose binding was largely entropically driven. We solved the crystal structures of EXLX1 complexed with cellulose-like oligosaccharides to find that EXLX1 binds the ligands through hydrophobic interactions of three linearly arranged aromatic residues in D2. The crystal structures revealed a unique form of ligand-mediated dimerization, with the oligosaccharide sandwiched between two D2 domains in opposite polarity. This report clarifies the molecular target of expansin and the specific molecular interactions of a type-A CBM with cellulose.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802, USA.