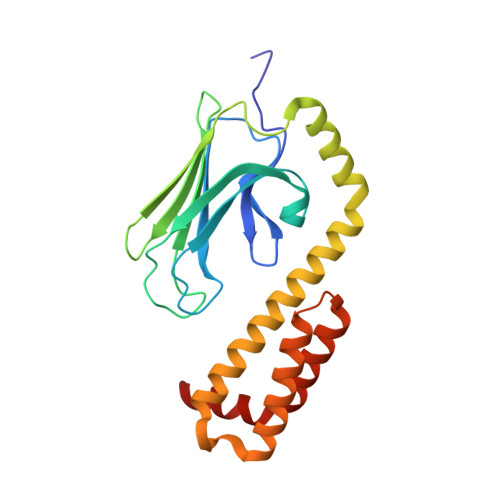
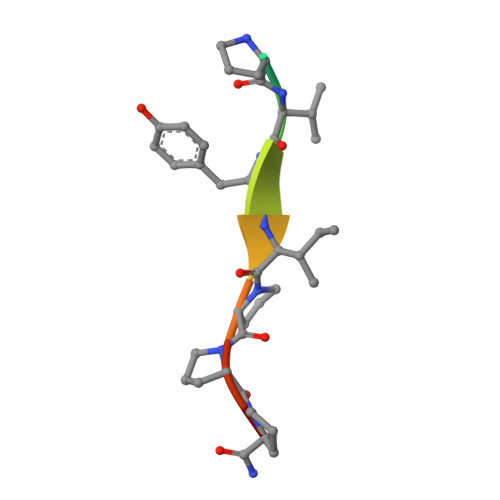
Structural Studies on the Forward and Reverse Binding Modes of Peptides to the Chaperone DnaK.
Zahn, M., Berthold, N., Kieslich, B., Knappe, D., Hoffmann, R., Strater, N.(2013) J Mol Biol 425: 2463-2479
- PubMed: 23562829
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2013.03.041
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4EZN, 4EZO, 4EZP, 4EZQ, 4EZR, 4EZT, 4EZW, 4EZX, 4EZY, 4EZZ, 4F00, 4F01, 4HY9, 4HYB - PubMed Abstract:
Hsp70 chaperones have been implicated in assisting protein folding of newly synthesized polypeptide chains, refolding of misfolded proteins, and protein trafficking. For these functions, the chaperones need to exhibit a significant promiscuity in binding to different sequences of hydrophobic peptide stretches. To characterize the structural basis of sequence specificity and flexibility of the Escherichia coli Hsp70 chaperone DnaK, we have analyzed crystal structures of the substrate binding domain of the protein in complex with artificially designed peptides as well as small proline-rich antimicrobial peptides. The latter peptides from mammals and insects were identified to target DnaK after cell penetration. Interestingly, the complex crystal structures reveal two different peptide binding modes. The peptides can bind either in a forward or in a reverse direction to the conventional substrate binding cleft of DnaK in an extended conformation. Superposition of the two binding modes shows a remarkable similarity in the side chain orientations and hydrogen bonding pattern despite the reversed peptide orientation. The DnaK chaperone has evolved to bind peptides in both orientations in the substrate binding cleft with comparable energy without rearrangements of the protein. Optimal hydrophobic interactions with binding pockets -2 to 0 appear to be the main determinant for the orientation and sequence position of peptide binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Bioanalytical Chemistry, Center for Biotechnology and Biomedicine, University of Leipzig, 04103 Leipzig, Germany.