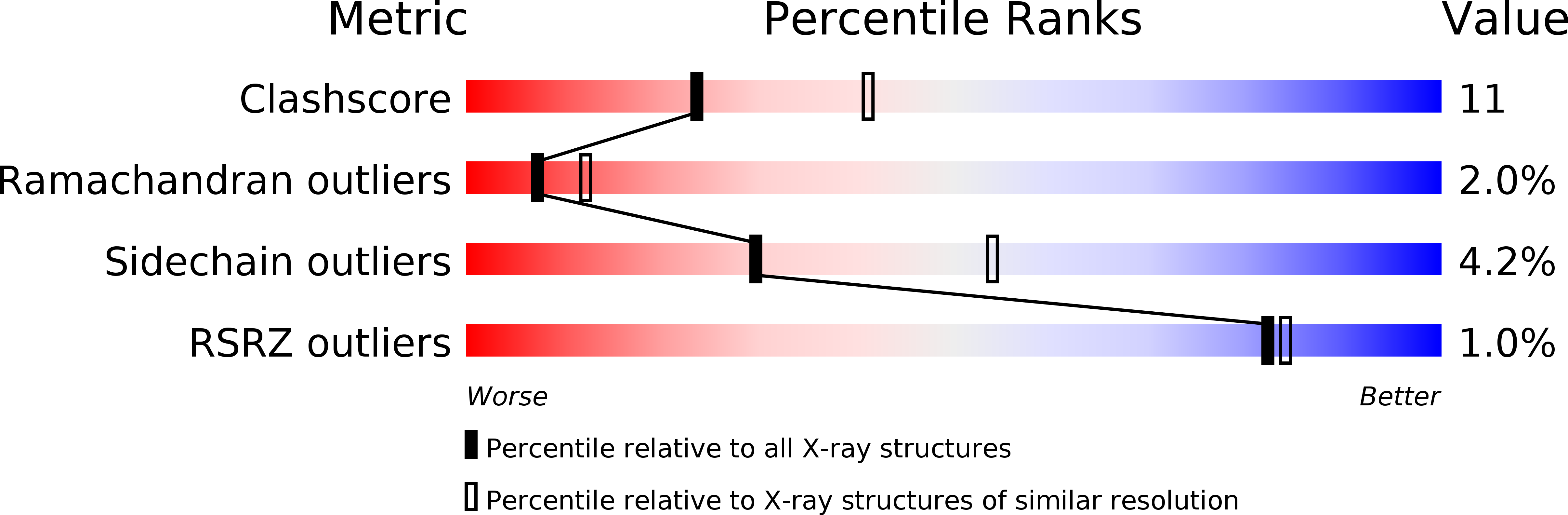
Crystal structure of the interferon gamma receptor alpha chain from chicken reveals an undetected extra helix compared with the human counterparts.
Ping, Z., Qi, J., Sun, Y., Lu, G., Shi, Y., Wang, X., Gao, G.F., Wang, M.(2014) J Interferon Cytokine Res 34: 41-51
- PubMed: 24283193
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2012.0160
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4EQ2, 4EQ3 - PubMed Abstract:
Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) is an important cytokine that induces antiviral, antiproliferative, and immunomodulatory effects on target cells, and is also crucial in the early defense against intracellular parasites, such as Listeria monocytogenes and Toxoplasma gondii. The biological activity of IFN-γ relies upon the formation of a complex with its 2 receptors, the interferon gamma alpha chain (IFNGR1) and beta chain (IFNGR2), which are type II cytokine receptors. Structural models of ligand-receptor interaction and complex structure of chicken IFNs with their receptors have remained elusive. Here we report the first structure of Gallus gallus (chicken) IFNGR1 (chIFNGR1) at 2.0 Å by molecule replacement according to the structure of selenomethionine substituted chIFNGR1. The structural comparison reveals its structural similarities with other class II cytokine receptors, despite divergent primary sequences. We further investigate the ligand-receptor interaction properties of chicken IFN-γ (chIFN-γ) and chIFNGR1 using size-exclusion chromatography and surface plasmon resonance techniques. These data aid in the understanding of the interaction of chicken (avian) IFN-γ with its receptors and its signal transduction.
Organizational Affiliation:
1 National Animal Protozoa Laboratory, Key Laboratory of Animal Epidemiology and Zoonosis of the Ministry of Agriculture, College of Veterinary Medicine, China Agricultural University , Beijing, China .