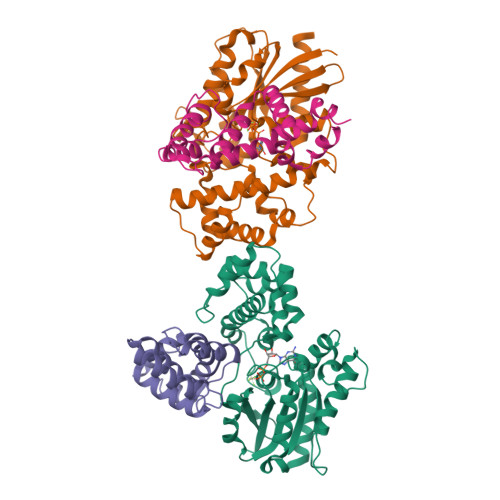
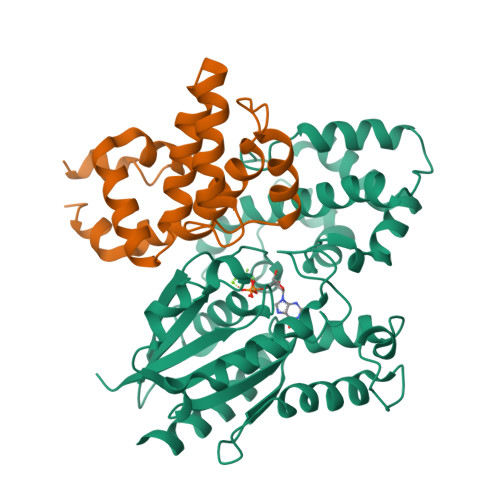
Structural and functional analysis of the regulator of G protein signaling 2-g alpha q complex.
Nance, M.R., Kreutz, B., Tesmer, V.M., Sterne-Marr, R., Kozasa, T., Tesmer, J.J.(2013) Structure 21: 438-448
- PubMed: 23434405
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2012.12.016
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4EKC, 4EKD - PubMed Abstract:
The heterotrimeric G protein Gαq is a key regulator of blood pressure, and excess Gαq signaling leads to hypertension. A specific inhibitor of Gαq is the GTPase activating protein (GAP) known as regulator of G protein signaling 2 (RGS2). The molecular basis for how Gαq/11 subunits serve as substrates for RGS proteins and how RGS2 mandates its selectivity for Gαq is poorly understood. In crystal structures of the RGS2-Gαq complex, RGS2 docks to Gαq in a different orientation from that observed in RGS-Gαi/o complexes. Despite its unique pose, RGS2 maintains canonical interactions with the switch regions of Gαq in part because its α6 helix adopts a distinct conformation. We show that RGS2 forms extensive interactions with the α-helical domain of Gαq that contribute to binding affinity and GAP potency. RGS subfamilies that do not serve as GAPs for Gαq are unlikely to form analogous stabilizing interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Life Sciences Institute, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-2216, USA.