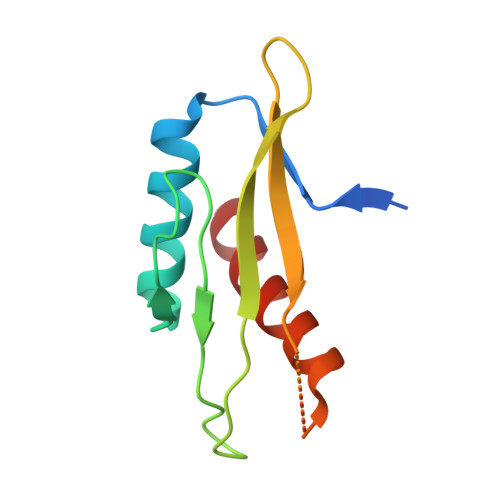
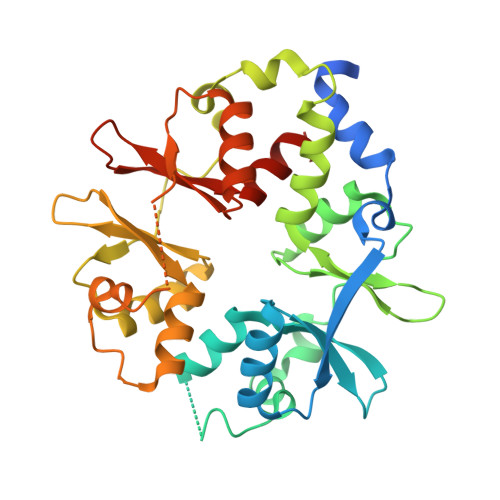
AMP-activated protein kinase undergoes nucleotide-dependent conformational changes
Chen, L., Wang, J., Zhang, Y.-Y., Yan, S.F., Neumann, D., Schlattner, U., Wang, Z.-X., Wu, J.-W.(2012) Nat Struct Mol Biol 19: 716-718
- PubMed: 22659875
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2319
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4EAG, 4EAI, 4EAJ, 4EAK, 4EAL - PubMed Abstract:
The energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a heterotrimeric complex that is allosterically activated by AMP binding to the γ subunit. Cocrystal structures of the mammalian AMPK core reveal occlusion of nucleotide-binding site 3 of the γ subunit in the presence of ATP. However, site 3 is occupied in the presence of AMP. Mutagenesis studies indicate that sites 3 and 4 are important for AMPK allosteric activation.
Organizational Affiliation:
MOE Key Laboratory of Protein Sciences, Tsinghua-Peking Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.