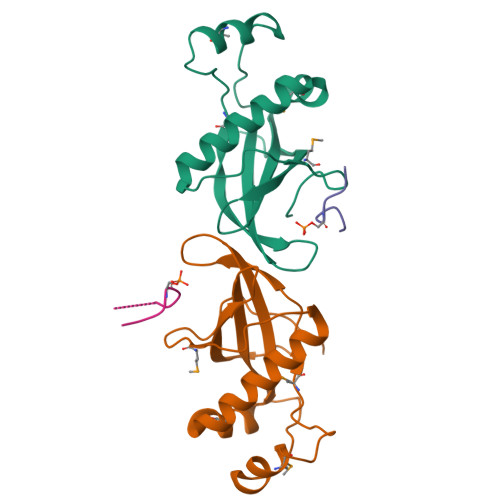
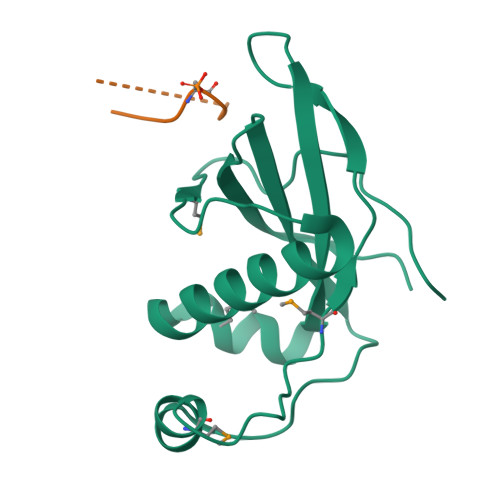
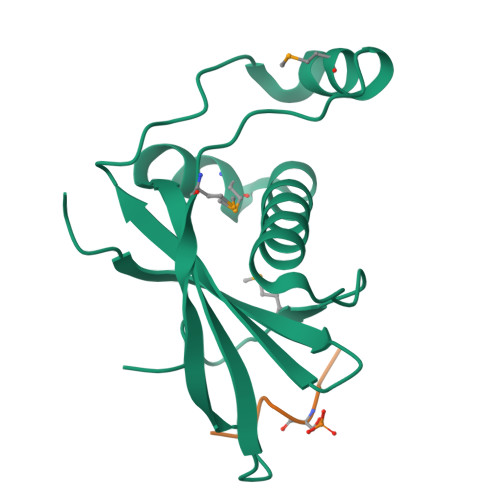
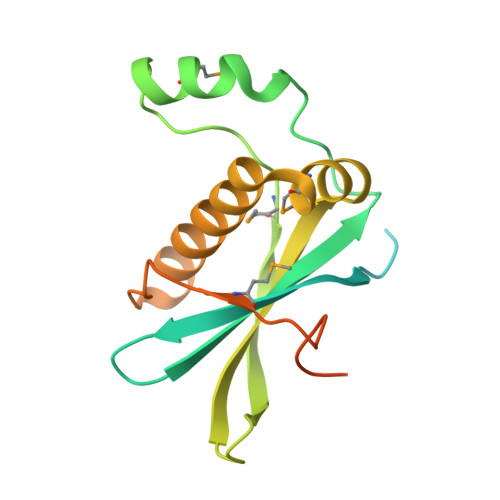
Structural Basis for Phosphorylation-Dependent Recruitment of Tel2 to Hsp90 by Pih1.
Pal, M., Morgan, M., Phelps, S.E., Roe, S.M., Parry-Morris, S., Downs, J.A., Polier, S., Pearl, L.H., Prodromou, C.(2014) Structure 22: 805
- PubMed: 24794838
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2014.04.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4CGU, 4CGV, 4CGW, 4CHH, 4CKT, 4CSE, 4CV4 - PubMed Abstract:
Client protein recruitment to the Hsp90 system depends on cochaperones that bind the client and Hsp90 simultaneously and facilitate their interaction. Hsp90 involvement in the assembly of snoRNPs, RNA polymerases, PI3-kinase-like kinases, and chromatin remodeling complexes depends on the TTT (Tel2-Tti1-Tti2), and R2TP complexes-consisting of the AAA-ATPases Rvb1 and Rvb2, Tah1 (Spagh/RPAP3 in metazoa), and Pih1 (Pih1D1 in humans)-that together provide the connection to Hsp90. The biochemistry underlying R2TP function is still poorly understood. Pih1 in particular, at the heart of the complex, has not been described at a structural level, nor have the multiple protein-protein interactions it mediates been characterized. Here we present a structural and biochemical analysis of Hsp90-Tah1-Pih1, Hsp90-Spagh, and Pih1D1-Tel2 complexes that reveal a domain in Pih1D1 specific for binding CK2 phosphorylation sites, and together define the structural basis by which the R2TP complex connects the Hsp90 chaperone system to the TTT complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
MRC Genome Damage and Stability Centre, School of Life Sciences, University of Sussex, Falmer, Brighton BN1 9RQ, UK.