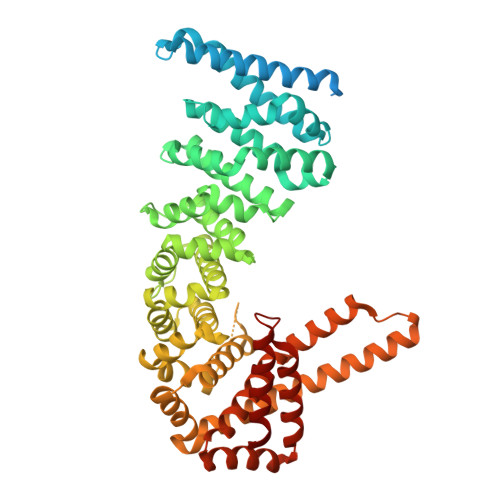
Structural and Mutational Analysis Reveals that Ctnnbl1 Binds Nlss in a Manner Distinct from that of its Closest Armadillo-Relative, Karyopherin Alpha
Ganesh, K., Maldegem, F.V., Telerman, S.B., Simpson, P., Johnson, C.M., Williams, R.L., Neuberger, M.S., Rada, C.(2014) FEBS Lett 588: 21
- PubMed: 24269683
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2013.11.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4CB8, 4CB9, 4CBA - PubMed Abstract:
CTNNBL1 is a spliceosome-associated protein that binds nuclear localization signals (NLSs) in splice factors CDC5L and Prp31 as well as the antibody diversifying enzyme AID. Here, crystal structures of human CTNNBL1 reveal a distinct structure from its closest homologue karyopherin-α. CTNNBL1 comprises a HEAT-like domain (including a nuclear export signal), a central armadillo domain, and a coiled-coil C-terminal domain. Structure-guided mutations of the region homologous to the karyopherin-α NLS-binding site fail to disrupt CTNNBL1-NLS interactions. Our results identify CTNNBL1 as a unique selective NLS-binding protein with striking differences from karyopherin-αs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Francis Crick Avenue, Cambridge CB2 0QH, UK.