Biochemical Analysis and Structure Determination of Paucimonas Lemoignei Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) (Phb) Depolymerase Phaz7 Muteins Reveal the Phb Binding Site and Details of Substrate-Enzyme Interactions.
Jendrossek, D., Hermawan, S., Subedi, B., Papageorgiou, A.C.(2013) Mol Microbiol 90: 649
- PubMed: 24007310
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.12391
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BRS, 4BTV, 4BVJ, 4BVK, 4BVL, 4BYM - PubMed Abstract:
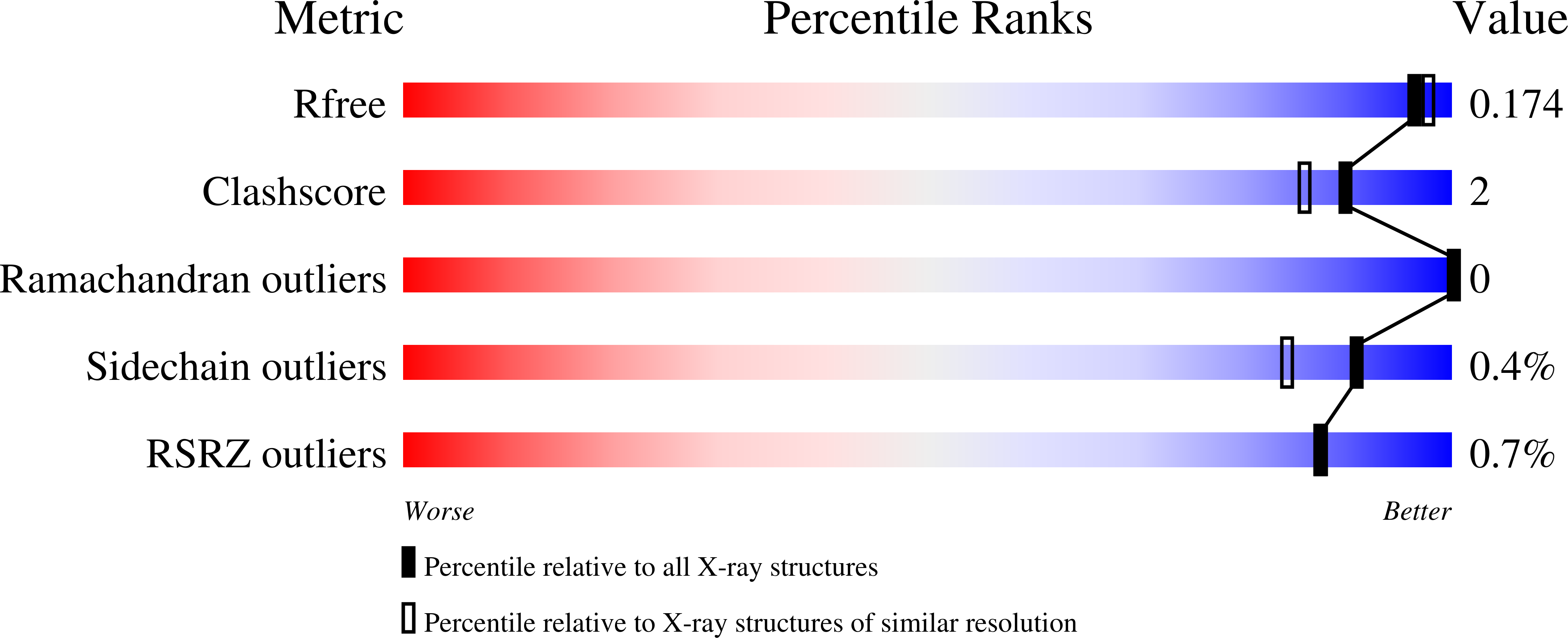
Five amino acids (Y105, Y176, Y189, Y189, W207) that constitute the substrate binding site of PHB depolymerase PhaZ7 were identified. All residues are located at a single surface-exposed location of PhaZ7. Exchange of these amino acids by less hydrophobic, hydrophilic or negatively charged residues reduced binding of PhaZ7 to PHB. Modifications of other residues at the PhaZ7 surface (F9, Y66, Y103, Y124, Y169, Y172, Y173, F198, Y203, Y204, F251, W252) had no effect on substrate binding. The PhaZ7 wild-type protein, three muteins with single amino acid exchanges (Y105A, Y105E, Y190E), a PhaZ7 variant with deletion of residues 202-208, and PhaZ7 in which the active-site serine had been replaced by alanine (S136A) were crystallized and their structures were determined at 1.6-2.0 Å resolution. The structures were almost identical but revealed flexibility of some regions. Structural analysis of PhaZ7 (S136A) with bound 3-hydroxybutyrate tetramer showed that the substrate binds in a cleft that is composed of Y105, Y176, Y189 and Y190 and thus confirmed the data obtained by site-directed mutagenesis. To the best of our knowledge this is the first example in which the substrate binding site of a PHB depolymerase is documented at a molecular and structural level.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut für Mikrobiologie, Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany.