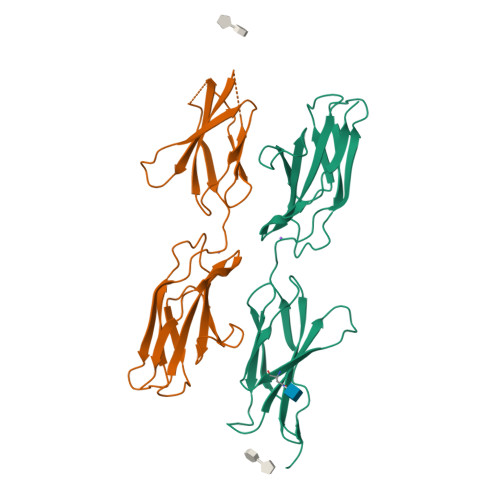
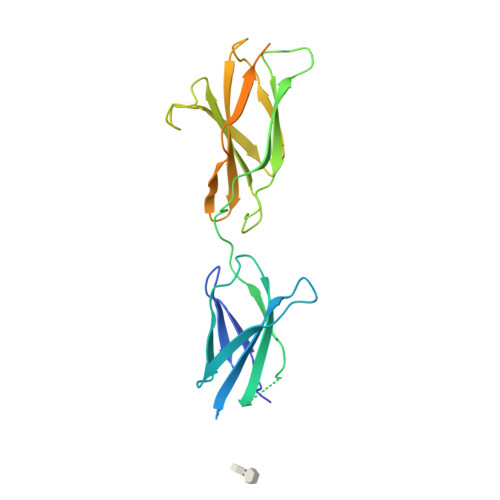
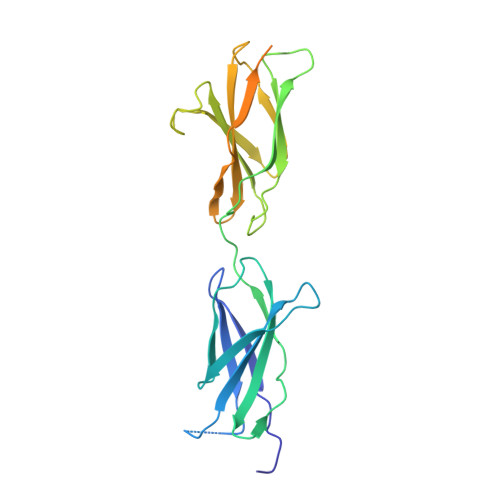
Structure of the Repulsive Guidance Molecule (Rgm)-Neogenin Signaling Hub
Bell, C.H., Healey, E., Van Erp, S., Bishop, B., Tang, C., Gilbert, R.J.C., Aricescu, A.R., Pasterkamp, R.J., Siebold, C.(2013) Science 341: 77
- PubMed: 23744777
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1232322
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BQ6, 4BQ7, 4BQ8, 4BQ9, 4BQB, 4BQC - PubMed Abstract:
Repulsive guidance molecule family members (RGMs) control fundamental and diverse cellular processes, including motility and adhesion, immune cell regulation, and systemic iron metabolism. However, it is not known how RGMs initiate signaling through their common cell-surface receptor, neogenin (NEO1). Here, we present crystal structures of the NEO1 RGM-binding region and its complex with human RGMB (also called dragon). The RGMB structure reveals a previously unknown protein fold and a functionally important autocatalytic cleavage mechanism and provides a framework to explain numerous disease-linked mutations in RGMs. In the complex, two RGMB ectodomains conformationally stabilize the juxtamembrane regions of two NEO1 receptors in a pH-dependent manner. We demonstrate that all RGM-NEO1 complexes share this architecture, which therefore represents the core of multiple signaling pathways.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Structural Biology, Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Roosevelt Drive, Oxford OX3 7BN, UK.