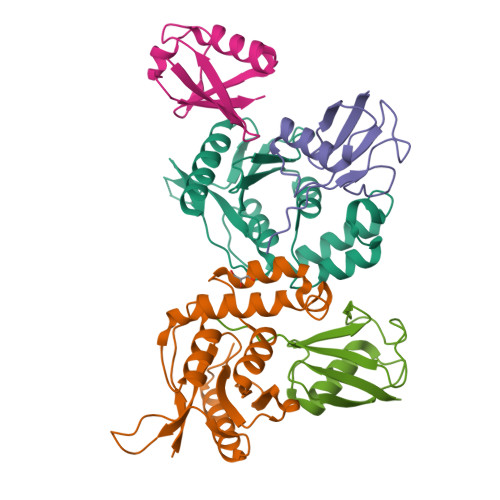
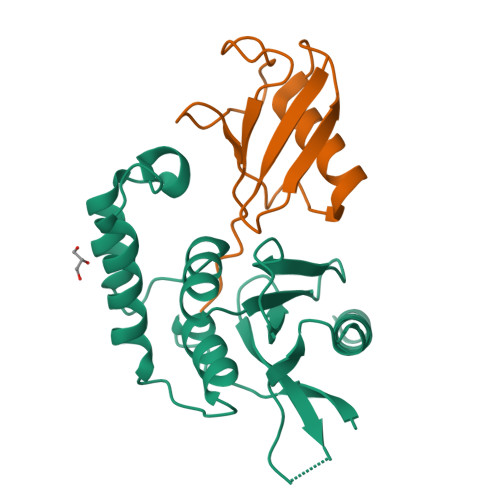
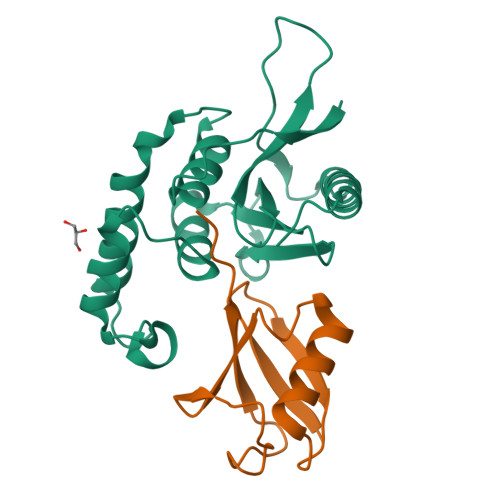
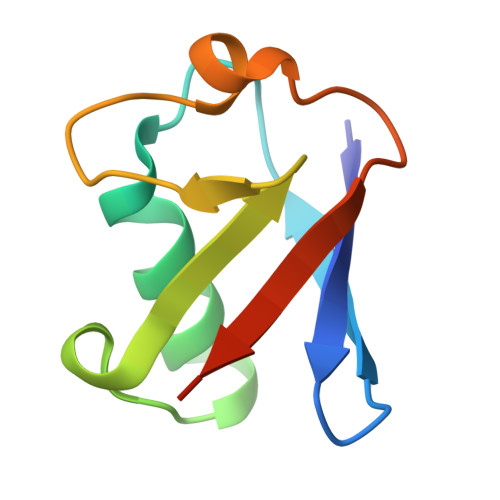
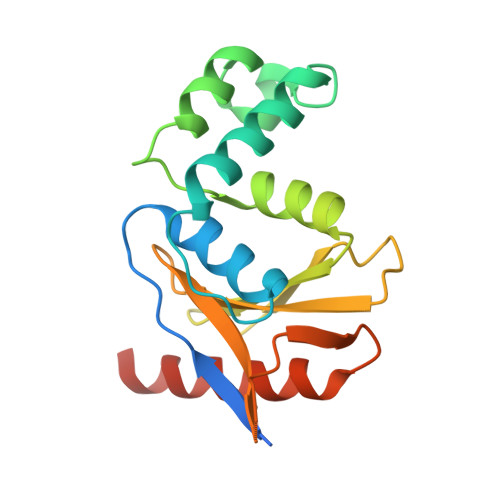
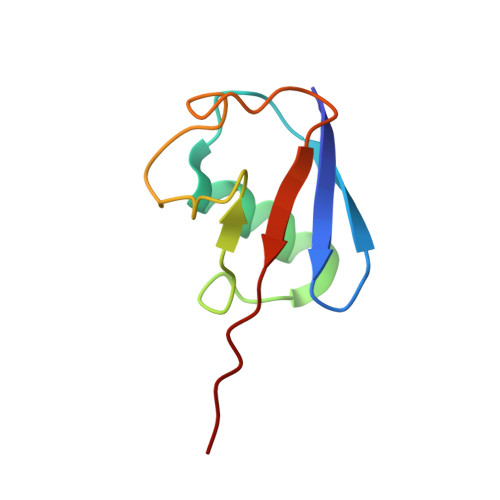
Otu Deubiquitinases Reveal Mechanisms of Linkage Specificity and Enable Ubiquitin Chain Restriction Analysis.
Mevissen, T.E.T., Hospenthal, M.K., Geurink, P.P., Elliott, P.R., Akutsu, M., Arnaudo, N., Ekkebus, R., Kulathu, Y., Wauer, T., El Oualid, F., Freund, S.M.V., Ovaa, H., Komander, D.(2013) Cell 154: 169
- PubMed: 23827681
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.046
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BOP, 4BOQ, 4BOS, 4BOU, 4BOZ - PubMed Abstract:
Sixteen ovarian tumor (OTU) family deubiquitinases (DUBs) exist in humans, and most members regulate cell-signaling cascades. Several OTU DUBs were reported to be ubiquitin (Ub) chain linkage specific, but comprehensive analyses are missing, and the underlying mechanisms of linkage specificity are unclear. Using Ub chains of all eight linkage types, we reveal that most human OTU enzymes are linkage specific, preferring one, two, or a defined subset of linkage types, including unstudied atypical Ub chains. Biochemical analysis and five crystal structures of OTU DUBs with or without Ub substrates reveal four mechanisms of linkage specificity. Additional Ub-binding domains, the ubiquitinated sequence in the substrate, and defined S1' and S2 Ub-binding sites on the OTU domain enable OTU DUBs to distinguish linkage types. We introduce Ub chain restriction analysis, in which OTU DUBs are used as restriction enzymes to reveal linkage type and the relative abundance of Ub chains on substrates.
Organizational Affiliation:
Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Francis Crick Avenue, Cambridge Biomedical Campus, Cambridge CB2 0QH, UK.