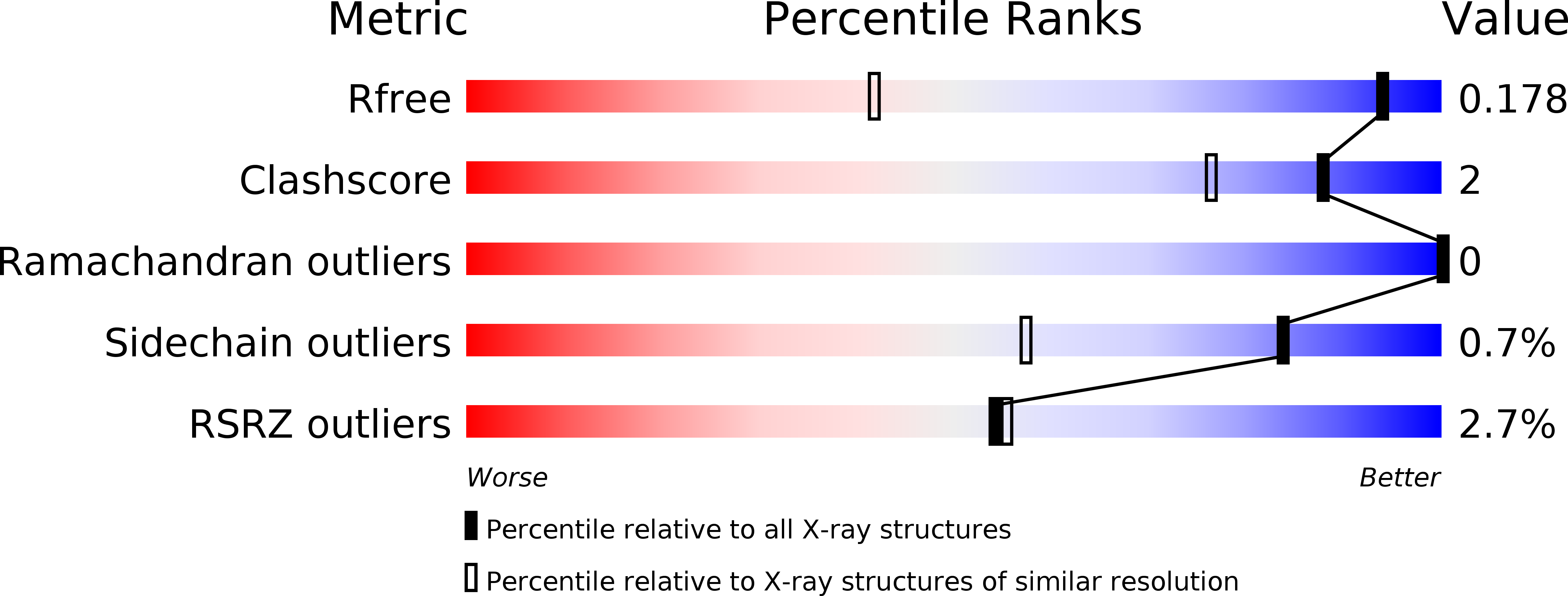
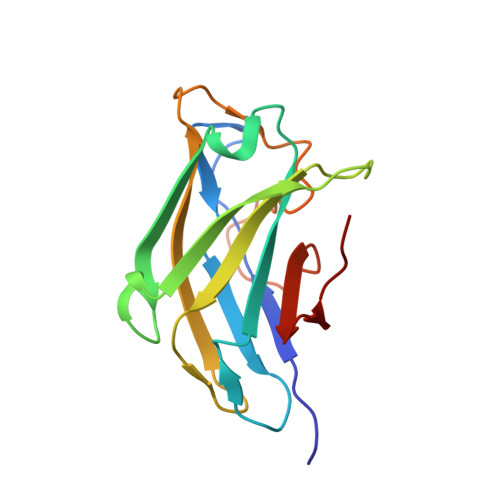
Fine-Structural Variance of Family 3 Carbohydrate-Binding Modules as Extracellular Biomass-Sensing Components of Clostridium Thermocellum Anti-Sigma(I) Factors.
Yaniv, O., Fichman, G., Borovok, I., Shoham, Y., Bayer, E.A., Lamed, R., Shimon, L.J.W., Frolow, F.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 522
- PubMed: 24531486
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S139900471302926X
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4B97, 4B9C, 4B9P - PubMed Abstract:
The anaerobic, thermophilic, cellulosome-producing bacterium Clostridium thermocellum relies on a variety of carbohydrate-active enzymes in order to efficiently break down complex carbohydrates into utilizable simple sugars. The regulation mechanism of the cellulosomal genes was unknown until recently, when genomic analysis revealed a set of putative operons in C. thermocellum that encode σI factors (i.e. alternative σ factors that control specialized regulon activation) and their cognate anti-σI factor (RsgI). These putative anti-σI-factor proteins have modules that are believed to be carbohydrate sensors. Three of these modules were crystallized and their three-dimensional structures were solved. The structures show a high overall degree of sequence and structural similarity to the cellulosomal family 3 carbohydrate-binding modules (CBM3s). The structures of the three carbohydrate sensors (RsgI-CBM3s) and a reference CBM3 are compared in the context of the structural determinants for the specificity of cellulose and complex carbohydrate binding. Fine structural variations among the RsgI-CBM3s appear to result in alternative substrate preferences for each of the sensors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, Tel Aviv University, 69978 Tel Aviv, Israel.