Insights Into the Oligomerization of Crmps: Crystal Structure of Human Collapsin Response Mediator Protein 5.
Ponnusamy, R., Lohkamp, B.(2013) J Neurochem 125: 855
- PubMed: 23373749
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12188
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4B90, 4B91, 4B92 - PubMed Abstract:
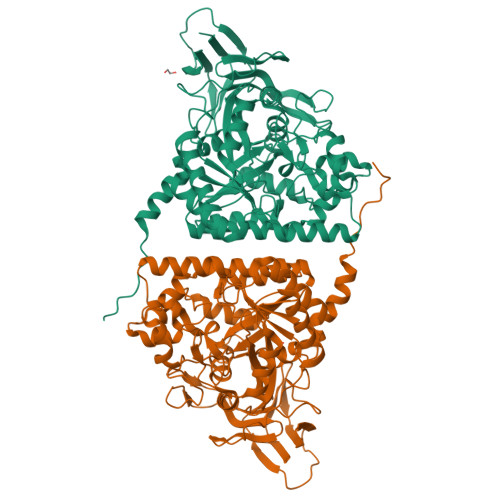
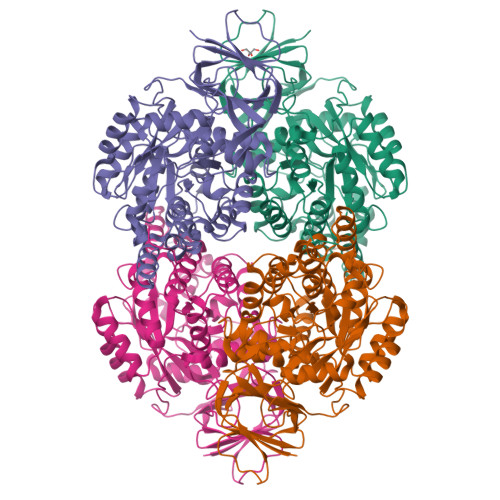
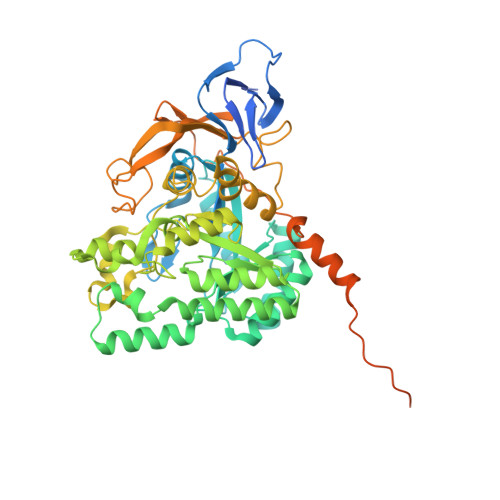
Collapsin response mediator protein-5 (CRMP-5) is the latest identified member of the CRMP cytosolic phosphoprotein family, which is crucial for neuronal development and repair. CRMPs exist as homo- and/or hetero-tetramers in vivo and participate in signaling transduction, cytoskeleton rearrangements, and endocytosis. CRMP-5 antagonizes many of the other CRMPs' functions either by directly interacting with them or by competing for their binding partners. We determined the crystal structures of a full length and a truncated version of human CRMP-5, both of which form a homo-tetramer similar to those observed in CRMP-1 and CRMP-2. However, solution studies indicate that CRMP-5 and CRMP-1 form weaker homo-tetramers compared with CRMP-2, and that divalent cations, Ca(2+) and Mg(2+), destabilize oligomers of CRMP-5 and CRMP-1, but promote CRMP-2 oligomerization. On the basis of comparative analysis of the CRMP-5 crystal structure, we identified residues that are crucial for determining the preference for hetero-oligomer or homo-oligomer formation. We also show that in spite of being the CRMP family member most closely related to dihydropyrimidinase, CRMP-5 does not have any detectable amidohydrolase activity. The presented findings provide new detailed insights into the structure, oligomerization, and regulation of CRMPs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.