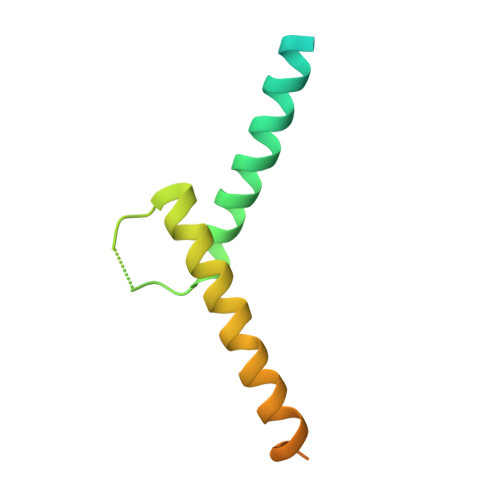
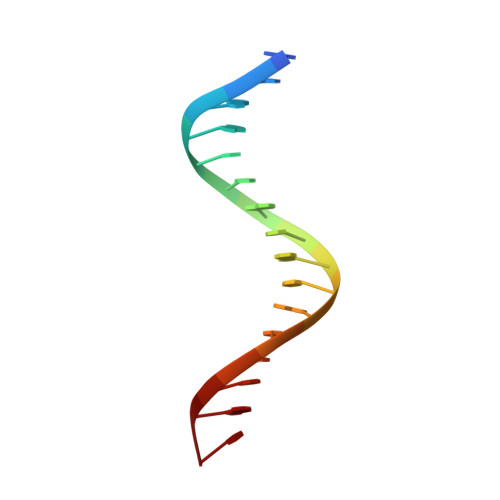
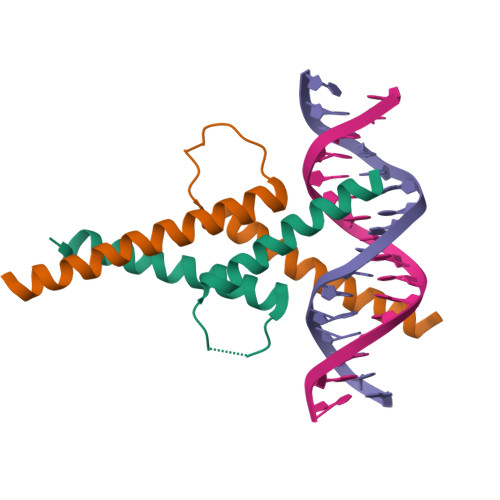
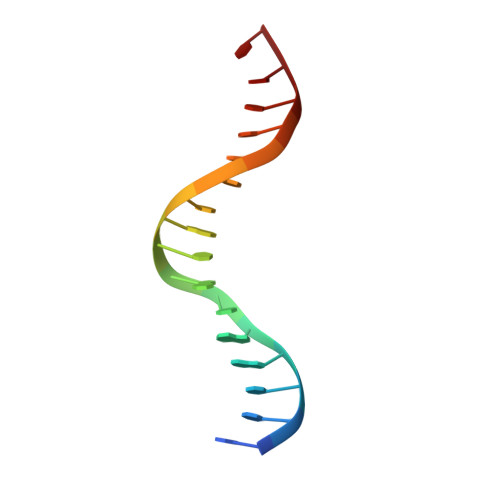
Restricted Leucine Zipper Dimerization and Specificity of DNA Recognition of the Melanocyte Master Regulator Mitf
Pogenberg, V., Hogmundsdottir, M., Bergsteinsdottir, K., Schepsky, A., Phung, B., Deineko, V., Milewski, M., Steingrimsson, E., Wilmanns, M.(2012) Genes Dev 26: 2647
- PubMed: 23207919
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.198192.112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4ATH, 4ATI, 4ATK - PubMed Abstract:
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) is a master regulator of melanocyte development and an important oncogene in melanoma. MITF heterodimeric assembly with related basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcription factors is highly restricted, and its binding profile to cognate DNA sequences is distinct. Here, we determined the crystal structure of MITF in its apo conformation and in the presence of two related DNA response elements, the E-box and M-box. In addition, we investigated mouse and human Mitf mutations to dissect the functional significance of structural features. Owing to an unusual three-residue shift in the leucine zipper register, the MITF homodimer shows a marked kink in one of the two zipper helices to allow an out-of-register assembly. Removal of this insertion relieves restricted heterodimerization by MITF and permits assembly with the transcription factor MAX. Binding of MITF to the M-box motif is mediated by an unusual nonpolar interaction by Ile212, a residue that is mutated in mice and humans with Waardenburg syndrome. As several related transcription factors have low affinity for the M-box sequence, our analysis unravels how these proteins discriminate between similar target sequences. Our data provide a rational basis for targeting MITF in the treatment of important hereditary diseases and cancer.
Organizational Affiliation:
European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Hamburg Unit, 22603 Hamburg, Germany.