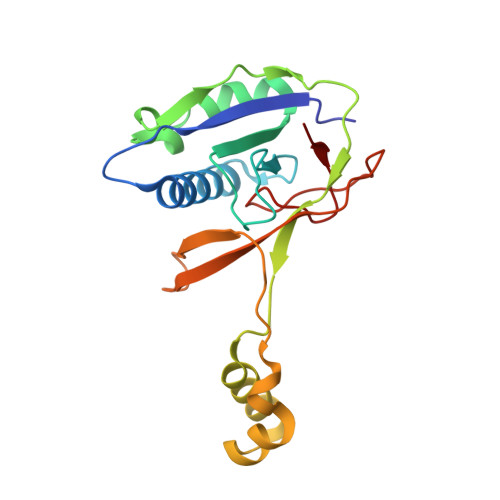
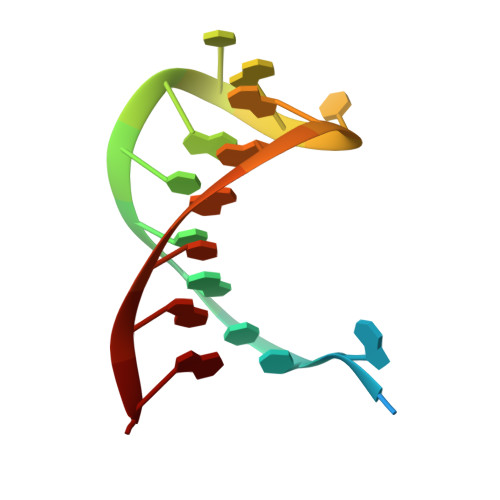
Csy4 Relies on an Unusual Catalytic Dyad to Position and Cleave Crispr RNA.
Haurwitz, R.E., Sternberg, S.H., Doudna, J.A.(2012) EMBO J 31: 2824
- PubMed: 22522703
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.107
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4AL5, 4AL6, 4AL7 - PubMed Abstract:
CRISPR-Cas adaptive immune systems protect prokaryotes against foreign genetic elements. crRNAs derived from CRISPR loci base pair with complementary nucleic acids, leading to their destruction. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, crRNA biogenesis requires the endoribonuclease Csy4, which binds and cleaves the repetitive sequence of the CRISPR transcript. Biochemical assays and three co-crystal structures of wild-type and mutant Csy4/RNA complexes reveal a substrate positioning and cleavage mechanism in which a histidine deprotonates the ribosyl 2'-hydroxyl pinned in place by a serine, leading to nucleophilic attack on the scissile phosphate. The active site catalytic dyad lacks a general acid to protonate the leaving group and positively charged residues to stabilize the transition state, explaining why the observed catalytic rate constant is ∼10(4)-fold slower than that of RNase A. We show that this RNA cleavage step is essential for assembly of the Csy protein-crRNA complex that facilitates target recognition. Considering that Csy4 recognizes a single cellular substrate and sequesters the cleavage product, evolutionary pressure has likely selected for substrate specificity and high-affinity crRNA interactions at the expense of rapid cleavage kinetics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley, 94720, USA.