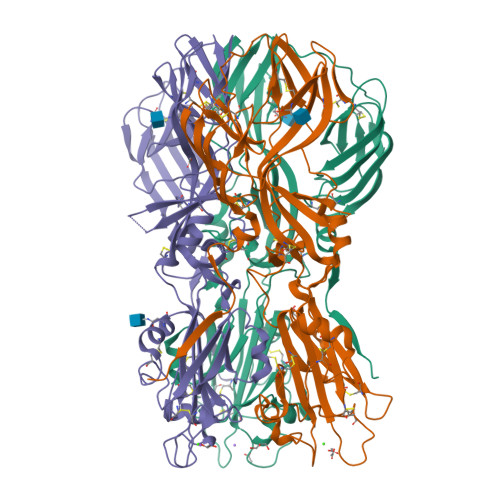
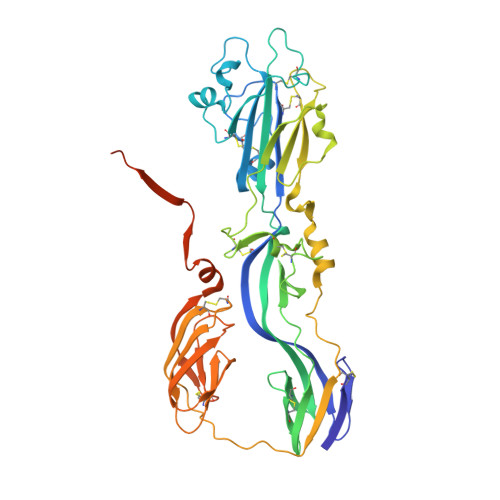
Functional and Evolutionary Insight from the Crystal Structure of Rubella Virus Protein E1.
Dubois, R.M., Vaney, M.C., Tortorici, M.A., Kurdi, R.A., Barba-Spaeth, G., Krey, T., Rey, F.A.(2013) Nature 493: 552
- PubMed: 23292515
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11741
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4ADG, 4ADI, 4ADJ, 4B3V - PubMed Abstract:
Little is known about the three-dimensional organization of rubella virus, which causes a relatively mild measles-like disease in children but leads to serious congenital health problems when contracted in utero. Although rubella virus belongs to the same family as the mosquito-borne alphaviruses, in many respects it is more similar to other aerosol-transmitted human viruses such as the agents of measles and mumps. Although the use of the triple MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) live vaccine has limited its incidence in western countries, congenital rubella syndrome remains an important health problem in the developing world. Here we report the 1.8 Å resolution crystal structure of envelope glycoprotein E1, the main antigen and sole target of neutralizing antibodies against rubella virus. E1 is the main player during entry into target cells owing to its receptor-binding and membrane-fusion functions. The structure reveals the epitope and the neutralization mechanism of an important category of protecting antibodies against rubella infection. It also shows that rubella virus E1 is a class II fusion protein, which had hitherto only been structurally characterized for the arthropod-borne alphaviruses and flaviviruses. In addition, rubella virus E1 has an extensive membrane-fusion surface that includes a metal site, reminiscent of the T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin family of cellular proteins that bind phosphatidylserine lipids at the plasma membrane of cells undergoing apoptosis. Such features have not been seen in any fusion protein crystallized so far. Structural comparisons show that the class II fusion proteins from alphaviruses and flaviviruses, despite belonging to different virus families, are closer to each other than they are to rubella virus E1. This suggests that the constraints on arboviruses imposed by alternating cycles between vertebrates and arthropods resulted in more conservative evolution. By contrast, in the absence of this constraint, the strictly human rubella virus seems to have drifted considerably into a unique niche as sole member of the Rubivirus genus.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut Pasteur, Département de Virologie, Unité de Virologie Structurale and CNRS URA 3015, F-75724 Paris Cedex 15, France.