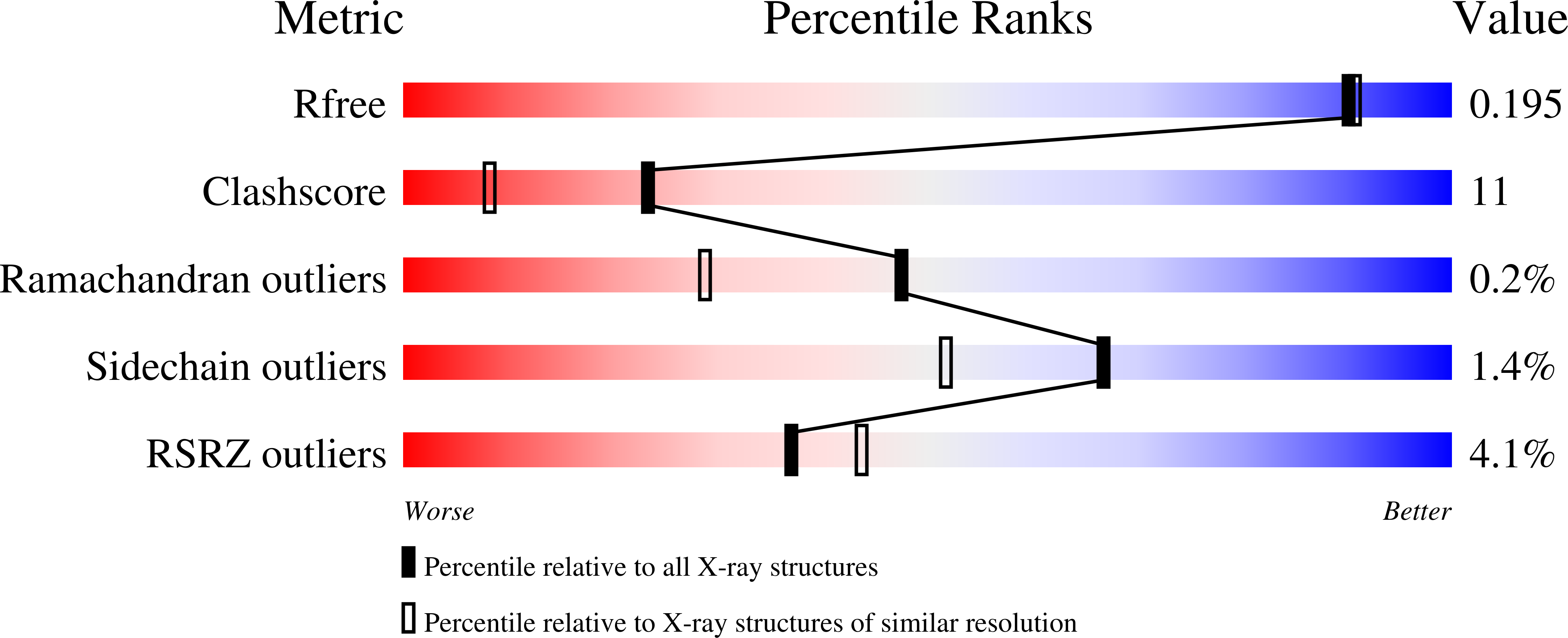
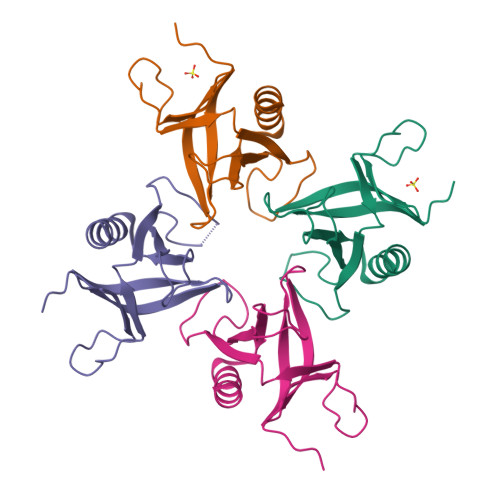
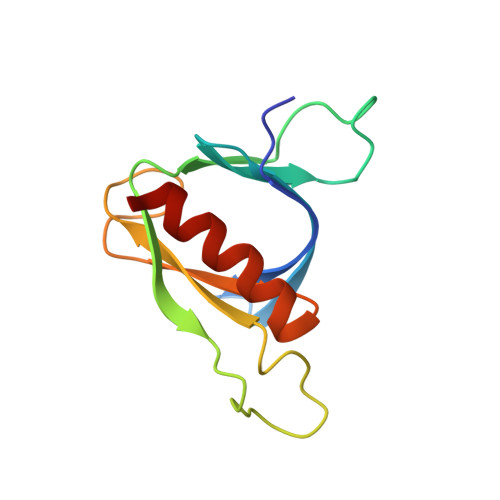
Structural Analyses of Slm1-Ph Domain Demonstrate Ligand Binding in the Non-Canonical Site
Anand, K., Maeda, K., Gavin, A.C.(2012) PLoS One 7: 36526
- PubMed: 22574179
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036526
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4A5K, 4A6F, 4A6H, 4A6K - PubMed Abstract:
Pleckstrin homology (PH) domains are common membrane-targeting modules and their best characterized ligands are a set of important signaling lipids that include phosphatidylinositol phosphates (PtdInsPs). PH domains recognize PtdInsPs through two distinct mechanisms that use different binding pockets on opposite sides of the β-strands 1 and 2: i) a canonical binding site delimited by the β1-β2 and β3-β4loops and ii) a non-canonical binding site bordered by the β1-β2 and β5-β6loops. The PH domain-containing protein Slm1 from budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for actin cytoskeleton polarization and cell growth. We recently reported that this PH domain binds PtdInsPs and phosphorylated sphingolipids in a cooperative manner. To study the structural basis for the Slm1-PH domain (Slm1-PH) specificity, we co-crystallized this domain with different soluble compounds that have structures analogous to anionic lipid head groups of reported Slm1 ligands: inositol 4-phosphate, which mimics phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PtdIns(4)P), and phosphoserine as a surrogate for dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate (DHS1-P). We found electron densities for the ligands within the so-called non-canonical binding site. An additional positively charged surface that contacts a phosphate group was identified next to the canonical binding site. Our results suggest that Slm1-PH utilizes a non-canonical binding site to bind PtdInsPs, similar to that described for the PH domains of β-spectrin, Tiam1 and ArhGAP9. Additionally, Slm1-PH may have retained an active canonical site. We propose that the presence of both a canonical and a non-canonical binding pocket in Slm1-PH may account for the cooperative binding to PtdInsPs and DHS-1P.
Organizational Affiliation:
European Molecular Biology Laboratory Heidelberg, Structural and Computational Biology Unit, Heidelberg, Germany. anand@embl.de