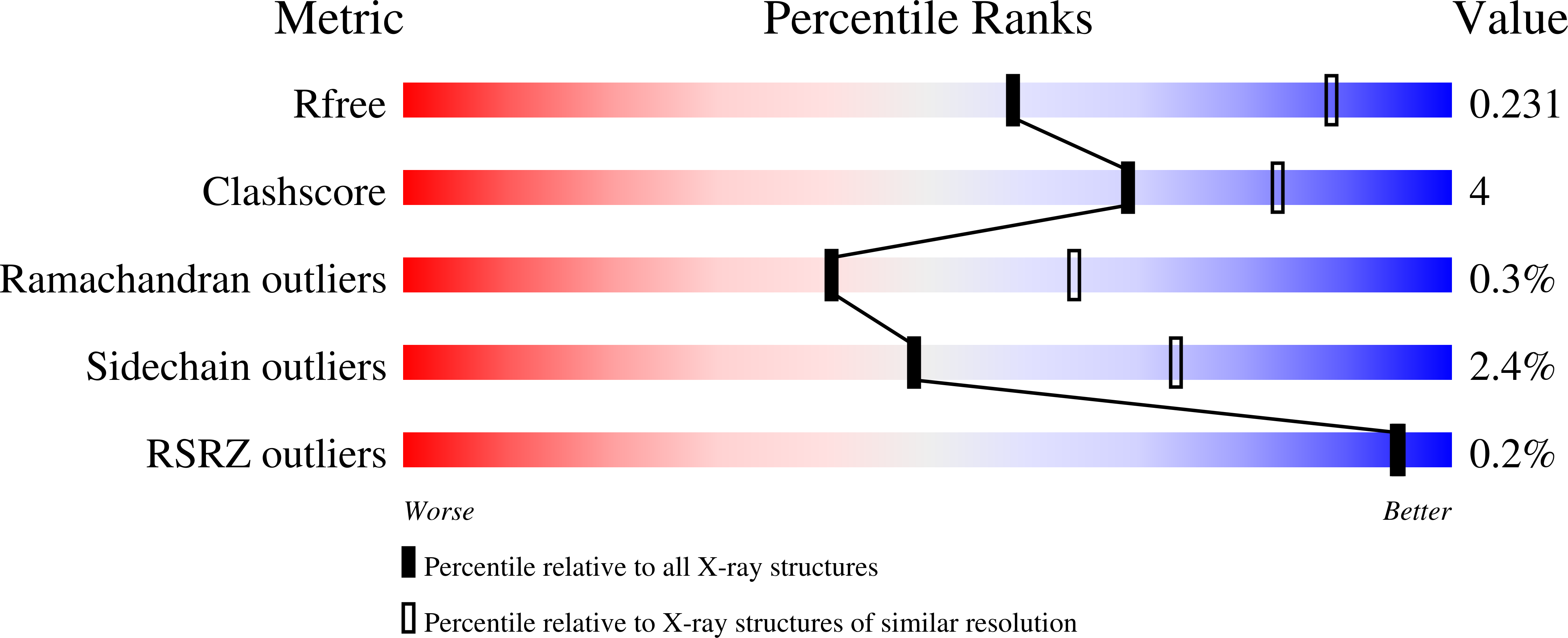
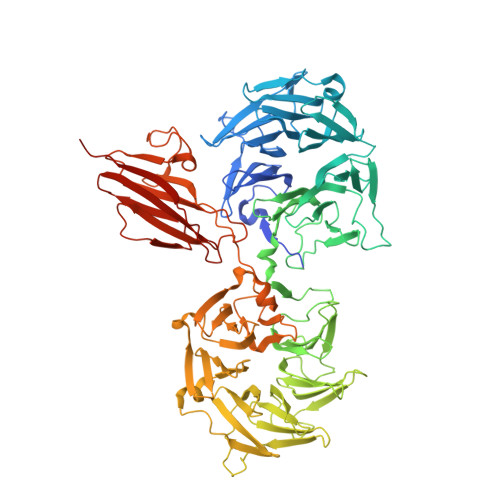
A Scissor Blade-Like Closing Mechanism Implicated in Transmembrane Signaling in a Bacteroides Hybrid Two-Component System.
Lowe, E.C., Basle, A., Czjzek, M., Firbank, S.J., Bolam, D.N.(2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 7298
- PubMed: 22532667
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200479109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4A2L, 4A2M - PubMed Abstract:
Signaling across the membrane in response to extracellular stimuli is essential for survival of all cells. In bacteria, responses to environmental changes are predominantly mediated by two-component systems, which are typically composed of a membrane-spanning sensor histidine kinase and a cytoplasmic response regulator. In the human gut symbiont Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, hybrid two-component systems are a key part of the bacterium's ability to sense and degrade complex carbohydrates in the gut. Here, we identify the activating ligand of the hybrid two-component system, BT4663, which controls heparin and heparan sulfate acquisition and degradation in this prominent gut microbe, and report the crystal structure of the extracellular sensor domain in both apo and ligand-bound forms. Current models for signal transduction across the membrane involve either a piston-like or rotational displacement of the transmembrane helices to modulate activity of the linked cytoplasmic kinases. The structures of the BT4663 sensor domain reveal a significant conformational change in the homodimer on ligand binding, which results in a scissor-like closing of the C-termini of each protomer. We propose this movement activates the attached intracellular kinase domains and represents an allosteric mechanism for bacterial transmembrane signaling distinct from previously described models, thus expanding our understanding of signal transduction across the membrane, a fundamental requirement in many important biological processes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Cell and Molecular Biosciences, Newcastle University, The Medical School, Newcastle upon Tyne NE2 4HH, United Kingdom.