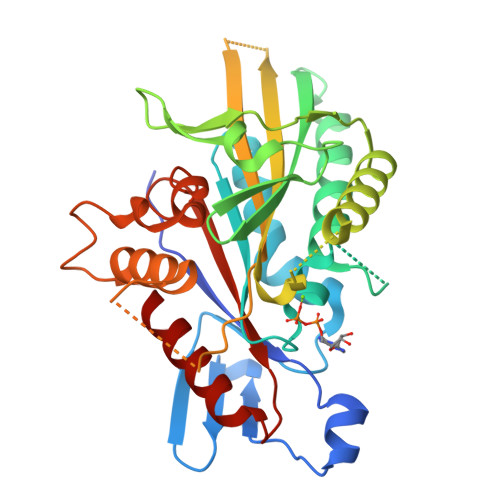
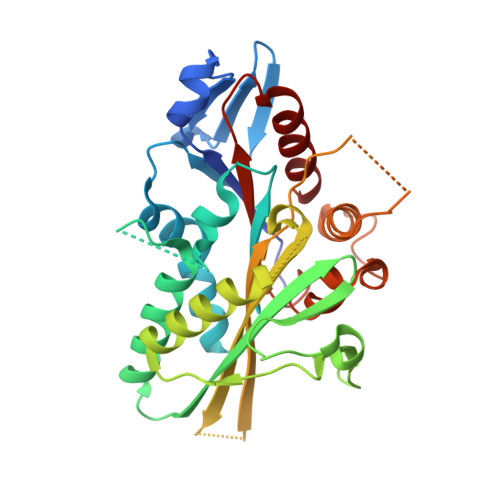
Structural Insights Into Human Kif7, a Kinesin Involved in Hedgehog Signalling.
Klejnot, M., Kozielski, F.(2012) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 68: 154
- PubMed: 22281744
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444911053042
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2XT3, 4A14 - PubMed Abstract:
Kif7, a member of the kinesin 4 superfamily, is implicated in a variety of diseases including Joubert, hydrolethalus and acrocallosal syndromes. It is also involved in primary cilium formation and the Hedgehog signalling pathway and may play a role in cancer. Its activity is crucial for embryonic development. Kif7 and Kif27, a closely related kinesin in the same subfamily, are orthologues of the Drosophila melanogaster kinesin-like protein Costal-2 (Cos2). In vertebrates, they work together to fulfil the role of the single Cos2 gene in Drosophila. Here, the high-resolution structure of the human Kif7 motor domain is reported and is compared with that of conventional kinesin, the founding member of the kinesin superfamily. These data are a first step towards structural characterization of a kinesin-4 family member and of this interesting molecular motor of medical significance.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Beatson Institute for Cancer Research, Garscube Estate, Switchback Road, Glasgow G61 1BD, Scotland. m.klejnot@beatson.gla.ac.uk