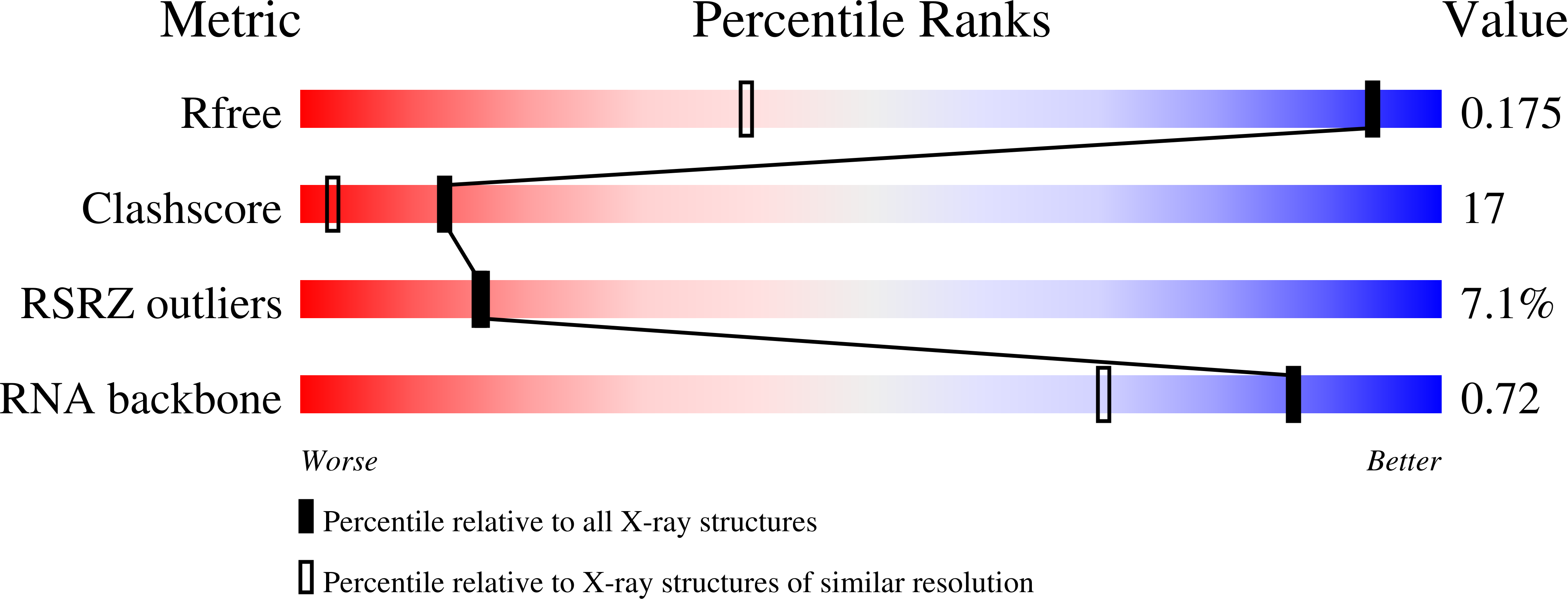Disorder and twin refinement of RNA heptamer double helices.
Mueller, U., Muller, Y.A., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sprinzl, M., Heinemann, U.(1999) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 55: 1405-1413
- PubMed: 10417408
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444999007441
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
464D, 466D - PubMed Abstract:
An RNA helix with seven base pairs which was derived from the acceptor stem of Escherichia coli tRNA(Ala), rGGGGCUA.rUAGCUCC (ALA(wt)), as well as a variant, rGGGGCUA.rUAGCCCC (ALA(C70)), in which the single G.U wobble base pair of ALA(wt) was replaced by G.C, crystallize in space group C2. Both non-isomorphic crystal forms display a complex packing pattern, which can be described alternatively as disorder or pseudo-merohedral twinning. The structure of ALA(wt) was determined by SIRAS phasing using an isomorphous iodine derivative, rGGGGCi(5)UA.rUAGCUCC (ALA(I)). All three RNA structures were subsequently subjected to twin refinement in space group P1, using anisotropic thermal displacement parameters at resolutions of 1.16, 1.23 and 1.4 A for ALA(wt), ALA(I) and ALA(C70), respectively. Alternatively, the structure of ALA(wt) was refined in space group C2 assuming twofold disorder of the molecular orientation. The refined structures are of reasonable quality according to all available indicators. There are no systematic differences between the molecular models resulting from twin refinement and disorder refinement.
Organizational Affiliation:
Forschungsgruppe Kristallographie, Max-Delbrück-Centrum für Molekulare Medizin, Robert-Rössle-Strasse 10, D-13092 Berlin, Germany.