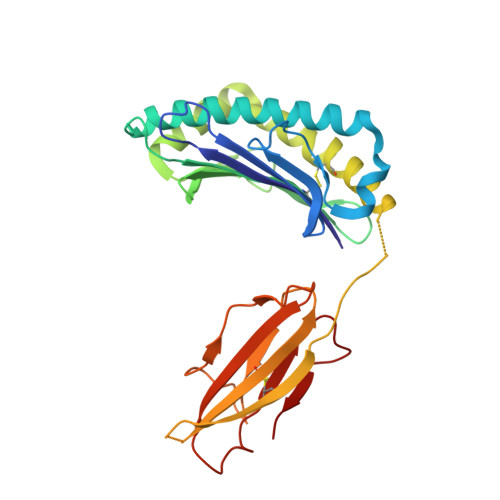
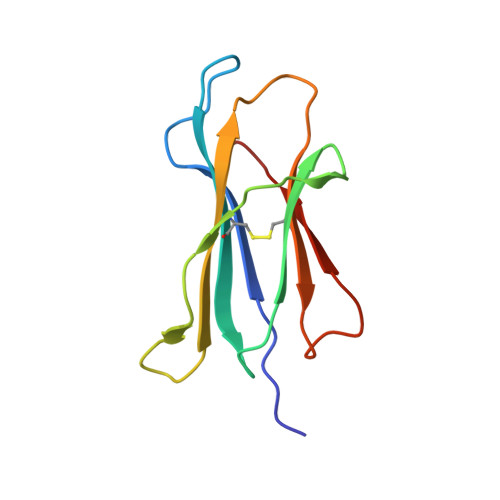
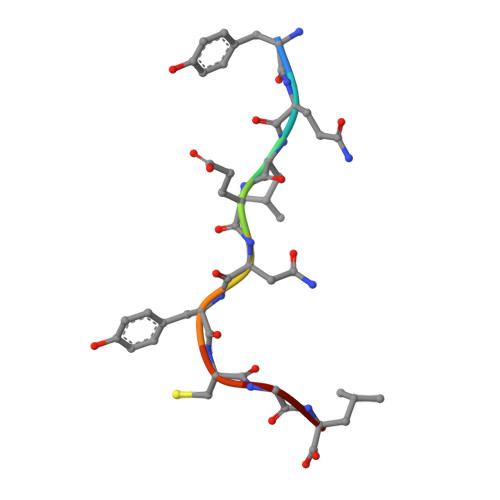
Compensatory mechanisms allow undersized anchor-deficient class I MHC ligands to mediate pathogenic autoreactive T cell responses
Lamont, D., Mukherjee, G., Kumar, P.R., Samanta, D., McPhee, C.G., Kay, T.W.H., Almo, S.C., DiLorenzo, T.P., Serreze, D.V.(2014) J Immunol 193: 2135-2146
- PubMed: 25063871
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1400997
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3WS3, 3WS6 - PubMed Abstract:
Self-reactive T cells must escape thymic negative selection to mediate pathogenic autoimmunity. In the NOD mouse model of autoimmune diabetes, several β cell-cytotoxic CD8 T cell populations are known, with the most aggressive of these represented by AI4, a T cell clone with promiscuous Ag-recognition characteristics. We identified a long-elusive β cell-specific ligand for AI4 as an unusually short H-2D(b)-binding 7-mer peptide lacking a C-terminal anchor residue and derived from the insulin A chain (InsA14-20). Crystallography reveals that compensatory mechanisms permit peptides lacking a C-terminal anchor to bind sufficiently to the MHC to enable destructive T cell responses, yet allow cognate T cells to avoid negative selection. InsA14-20 shares two solvent-exposed residues with previously identified AI4 ligands, providing a structural explanation for AI4's promiscuity. Detection of AI4-like T cells, using mimotopes of InsA14-20 with improved H-2D(b)-binding characteristics, establishes the AI4-like T cell population as a consistent feature of the islet infiltrates of NOD mice. Our work establishes undersized peptides as previously unrecognized targets of autoreactive CD8 T cells and presents a strategy for their further exploration as Ags in autoimmune disease.
- The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME 04609;
Organizational Affiliation: