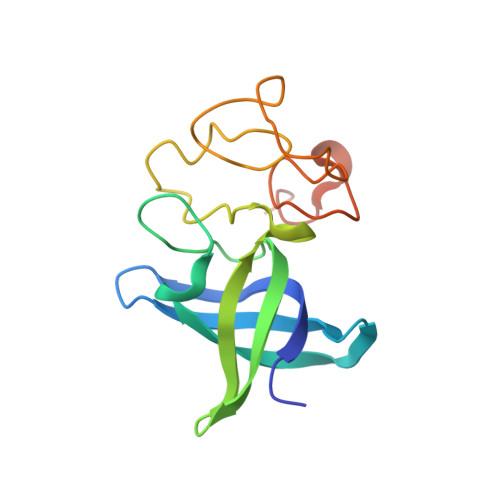
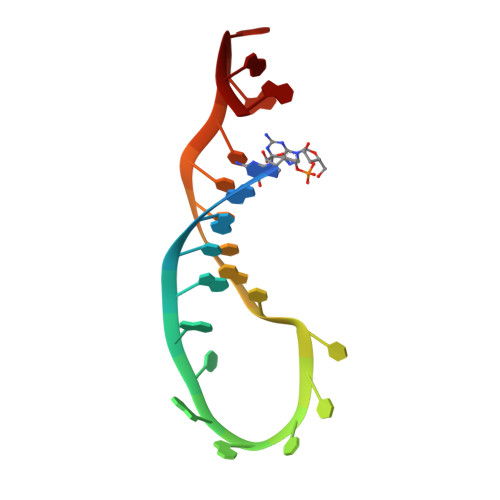
Molecular Basis for Interaction of let-7 MicroRNAs with Lin28.
Nam, Y., Chen, C., Gregory, R.I., Chou, J.J., Sliz, P.(2011) Cell 147: 1080-1091
- PubMed: 22078496
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3TRZ, 3TS0, 3TS2 - PubMed Abstract:
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNA molecules that regulate gene expression. Among these, members of the let-7 miRNA family control many cell-fate determination genes to influence pluripotency, differentiation, and transformation. Lin28 is a specific, posttranscriptional inhibitor of let-7 biogenesis. We report crystal structures of mouse Lin28 in complex with sequences from let-7d, let-7-f1, and let-7 g precursors. The two folded domains of Lin28 recognize two distinct regions of the RNA and are sufficient for inhibition of let-7 in vivo. We also show by NMR spectroscopy that the linker connecting the two folded domains is flexible, accommodating Lin28 binding to diverse let-7 family members. Protein-RNA complex formation imposes specific conformations on both components that could affect downstream recognition by other processing factors. Our data provide a molecular explanation for Lin28 specificity and a model for how it regulates let-7.
- Department of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: