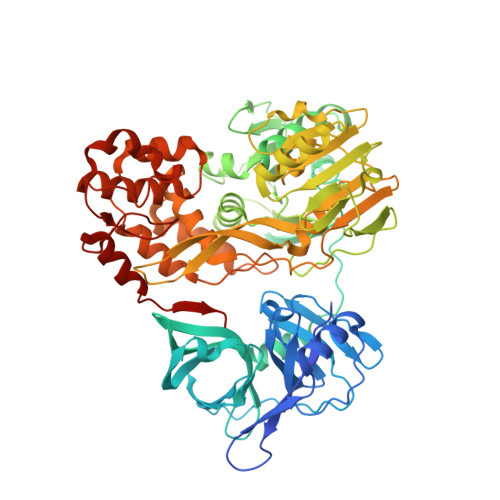
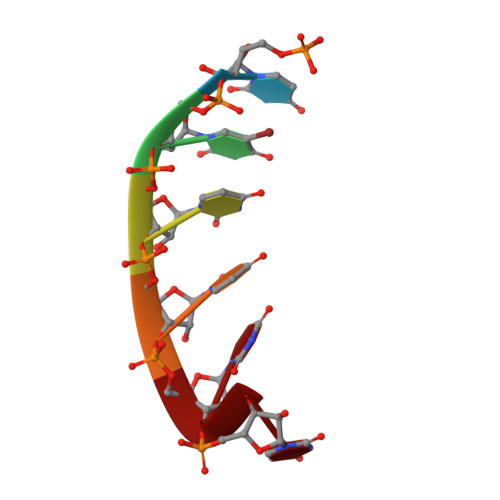
Visualizing ATP-Dependent RNA Translocation by the NS3 Helicase from HCV.
Appleby, T.C., Anderson, R., Fedorova, O., Pyle, A.M., Wang, R., Liu, X., Brendza, K.M., Somoza, J.R.(2011) J Mol Biology 405: 1139-1153
- PubMed: 21145896
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.11.034
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3O8B, 3O8C, 3O8D, 3O8R - PubMed Abstract:
The structural mechanism by which nonstructural protein 3 (NS3) from the hepatitis C virus (HCV) translocates along RNA is currently unknown. HCV NS3 is an ATP-dependent motor protein essential for viral replication and a member of the superfamily 2 helicases. Crystallographic analysis using a labeled RNA oligonucleotide allowed us to unambiguously track the positional changes of RNA bound to full-length HCV NS3 during two discrete steps of the ATP hydrolytic cycle. The crystal structures of HCV NS3, NS3 bound to bromine-labeled RNA, and a tertiary complex of NS3 bound to labeled RNA and a non-hydrolyzable ATP analog provide a direct view of how large domain movements resulting from ATP binding and hydrolysis allow the enzyme to translocate along the phosphodiester backbone. While directional translocation of HCV NS3 by a single base pair per ATP hydrolyzed is observed, the 3' end of the RNA does not shift register with respect to a conserved tryptophan residue, supporting a "spring-loading" mechanism that leads to larger steps by the enzyme as it moves along a nucleic acid substrate.
- Department of Structural Chemistry, Gilead Sciences, Inc., 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA. todd.appleby@gilead.com
Organizational Affiliation: