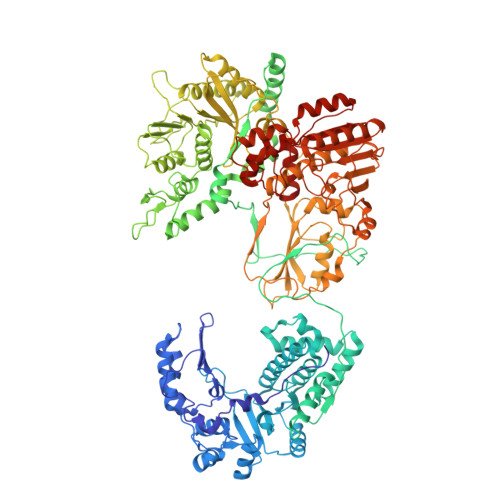
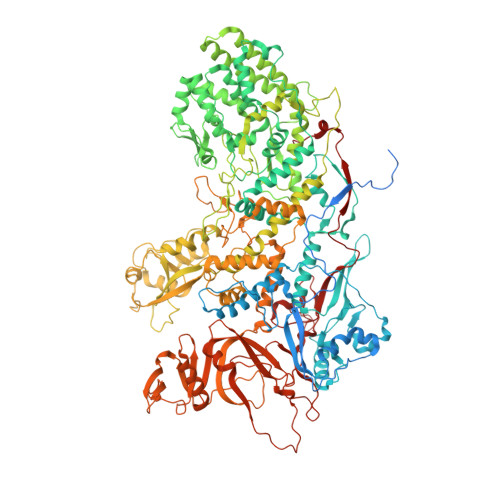
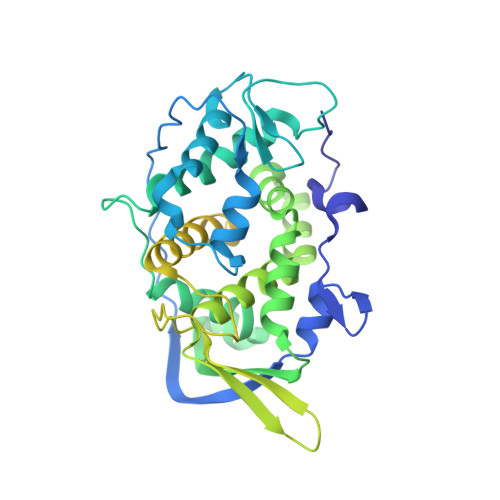
A putative ATPase mediates RNA transcription and capping in a dsRNA virus.
Yu, X., Jiang, J., Sun, J., Zhou, Z.H.(2015) Elife 4: e07901-e07901
- PubMed: 26240998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.07901
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3JAY, 3JAZ, 3JB0, 3JB1, 3JB2, 3JB3 - PubMed Abstract:
mRNA transcription in dsRNA viruses is a highly regulated process but the mechanism of this regulation is not known. Here, by nucleoside triphosphatase (NTPase) assay and comparisons of six high-resolution (2.9-3.1 Å) cryo-electron microscopy structures of cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus with bound ligands, we show that the large sub-domain of the guanylyltransferase (GTase) domain of the turret protein (TP) also has an ATP-binding site and is likely an ATPase. S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) acts as a signal and binds the methylase-2 domain of TP to induce conformational change of the viral capsid, which in turn activates the putative ATPase. ATP binding/hydrolysis leads to an enlarged capsid for efficient mRNA synthesis, an open GTase domain for His217-mediated guanylyl transfer, and an open methylase-1 domain for SAM binding and methyl transfer. Taken together, our data support a role of the putative ATPase in mediating the activation of mRNA transcription and capping within the confines of the virus.
- Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Molecular Genetics, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: