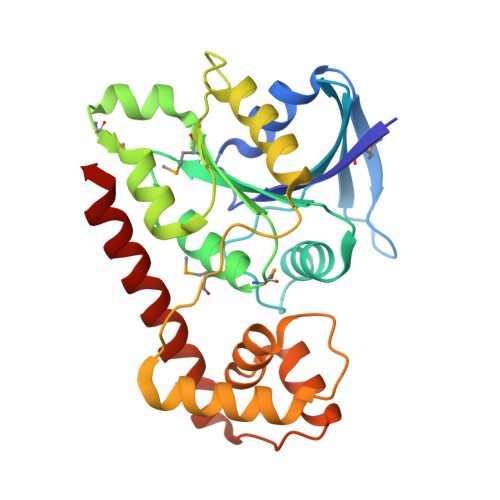
Structural basis of novel interactions between the small-GTPase and GDI-like domains in prokaryotic FeoB iron transporter
Hattori, M., Jin, Y., Nishimasu, H., Tanaka, Y., Mochizuki, M., Uchiumi, T., Ishitani, R., Ito, K., Nureki, O.(2009) Structure 17: 1345-1355
- PubMed: 19733088
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2009.08.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3A1S, 3A1T, 3A1U, 3A1V, 3A1W - PubMed Abstract:
The FeoB family proteins are widely distributed prokaryotic membrane proteins involved in Fe(2+) uptake. FeoB consists of N-terminal cytosolic and C-terminal transmembrane domains. The N-terminal region of the cytosolic domain is homologous to small GTPase (G) proteins and is considered to regulate Fe(2+) uptake. The spacer region connecting the G and TM domains reportedly functions as a GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI)-like domain that stabilizes the GDP-binding state. However, the function of the G and GDI-like domains in iron uptake remains unclear. Here, we report the structural and functional analyses of the FeoB cytosolic domain from Thermotoga maritima. The structure-based mutational analysis indicated that the interaction between the G and GDI-like domains is important for both the GDI and Fe(2+) uptake activities. On the basis of these results, we propose a regulatory mechanism of Fe(2+) uptake.
- Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo, Minato-ku, Tokyo, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: