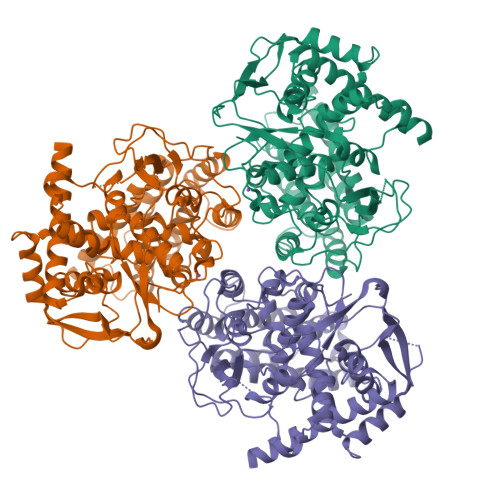
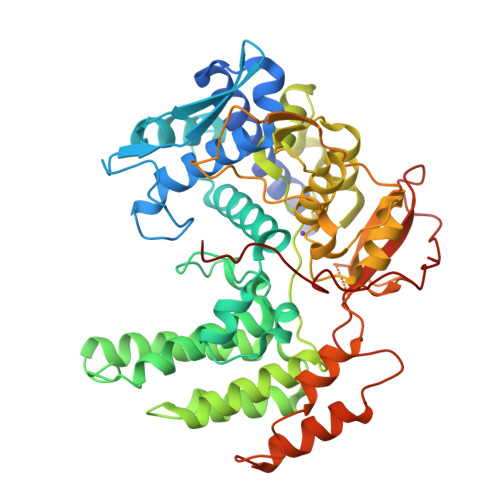
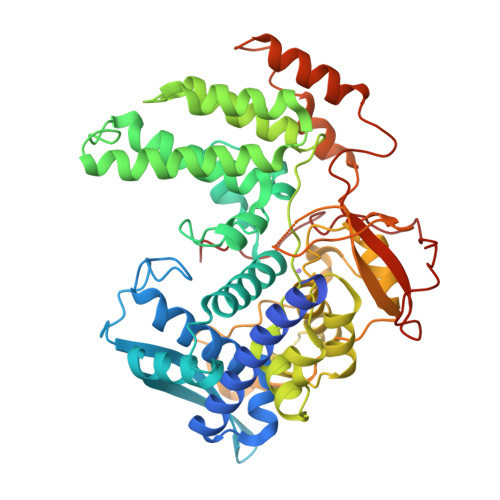
Monomeric Nucleoprotein of Influenza a Virus.
Chenavas, S., Estrozi, L.F., Slama-Schwok, A., Delmas, B., Di Primo, C., Baudin, F., Li, X., Crepin, T., Ruigrok, R.W.(2013) PLoS Pathog 9: 3275
- PubMed: 23555270
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003275
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ZDP - PubMed Abstract:
Isolated influenza A virus nucleoprotein exists in an equilibrium between monomers and trimers. Samples containing only monomers or only trimers can be stabilized by respectively low and high salt. The trimers bind RNA with high affinity but remain trimmers, whereas the monomers polymerise onto RNA forming nucleoprotein-RNA complexes. When wild type (wt) nucleoprotein is crystallized, it forms trimers, whether one starts with monomers or trimers. We therefore crystallized the obligate monomeric R416A mutant nucleoprotein and observed how the domain exchange loop that leads over to a neighbouring protomer in the trimer structure interacts with equivalent sites on the mutant monomer surface, avoiding polymerisation. The C-terminus of the monomer is bound to the side of the RNA binding surface, lowering its positive charge. Biophysical characterization of the mutant and wild type monomeric proteins gives the same results, suggesting that the exchange domain is folded in the same way for the wild type protein. In a search for how monomeric wt nucleoprotein may be stabilized in the infected cell we determined the phosphorylation sites on nucleoprotein isolated from virus particles. We found that serine 165 was phosphorylated and conserved in all influenza A and B viruses. The S165D mutant that mimics phosphorylation is monomeric and displays a lowered affinity for RNA compared with wt monomeric NP. This suggests that phosphorylation may regulate the polymerisation state and RNA binding of nucleoprotein in the infected cell. The monomer structure could be used for finding new anti influenza drugs because compounds that stabilize the monomer may slow down viral infection.
Organizational Affiliation:
UJF-EMBL-CNRS UMI 3265, Unit of Virus Host Cell Interactions, Grenoble, France.