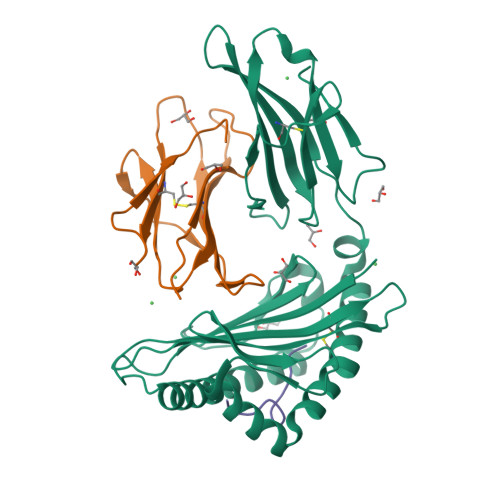
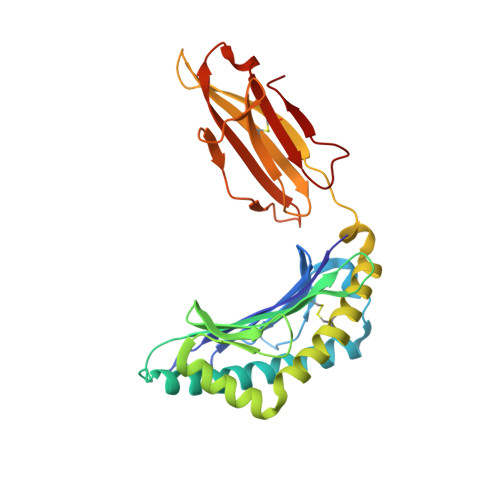
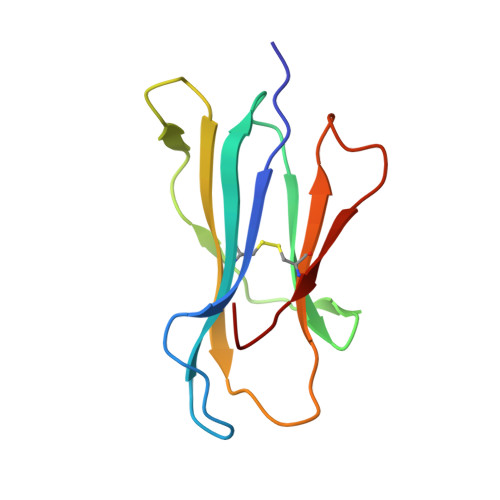
The impact of a large and frequent deletion in the human TCR beta locus on antiviral immunity
Brennan, R.M., Petersen, J., Neller, M.A., Miles, J.J., Burrows, J.M., Smith, C., McCluskey, J., Khanna, R., Rossjohn, J., Burrows, S.R.(2012) J Immunol 188: 2742-2748
- PubMed: 22323539
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1102675
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3VCL - PubMed Abstract:
The TCR plays a critical role in recognizing intracellular pathogens and initiating pathways leading to the destruction of infected cells by the immune system. Although genetic variability is known to greatly impact on the human immune system and the outcome of infection, the influence of sequence variation leading to the inactivation or deletion of TCR gene segments is unknown. To investigate this issue, we examined the CD8(+) T cell response to an HLA-B7-restricted epitope ((265)RPHERNGFTVL(275)) from the pp65 Ag of human CMV that was highly biased and frequently dominated by a public TCR β-chain encoded by the variable gene segment TRBV4-3. Approximately 40% of humans lack T cells expressing TRBV4-3 because of a 21.5-kb insertion/deletion polymorphism, but these individuals remain responsive to this epitope, using a diverse T cell repertoire characterized by private TCR usage. Although most residues within the bulged 11-mer peptide were accessible for TCR contact, the public and private TCRs showed distinct patterns of sensitivity to amino acid substitution at different positions within the peptide, thereby suggesting that the repertoire diversity generated in the absence of the dominant public TRBV4-3(+) TCR could lead to better protection from viral escape mutation. Thus, variation in the size of the TRBV repertoire clearly contributes toward interindividual variability in immune responses and is presumably maintained in many ethnic groups to enhance the diversity of Ag-specific T cell responses.
Organizational Affiliation:
Australian Centre for Vaccine Development, Queensland Institute of Medical Research, Brisbane, Queensland 4029, Australia.