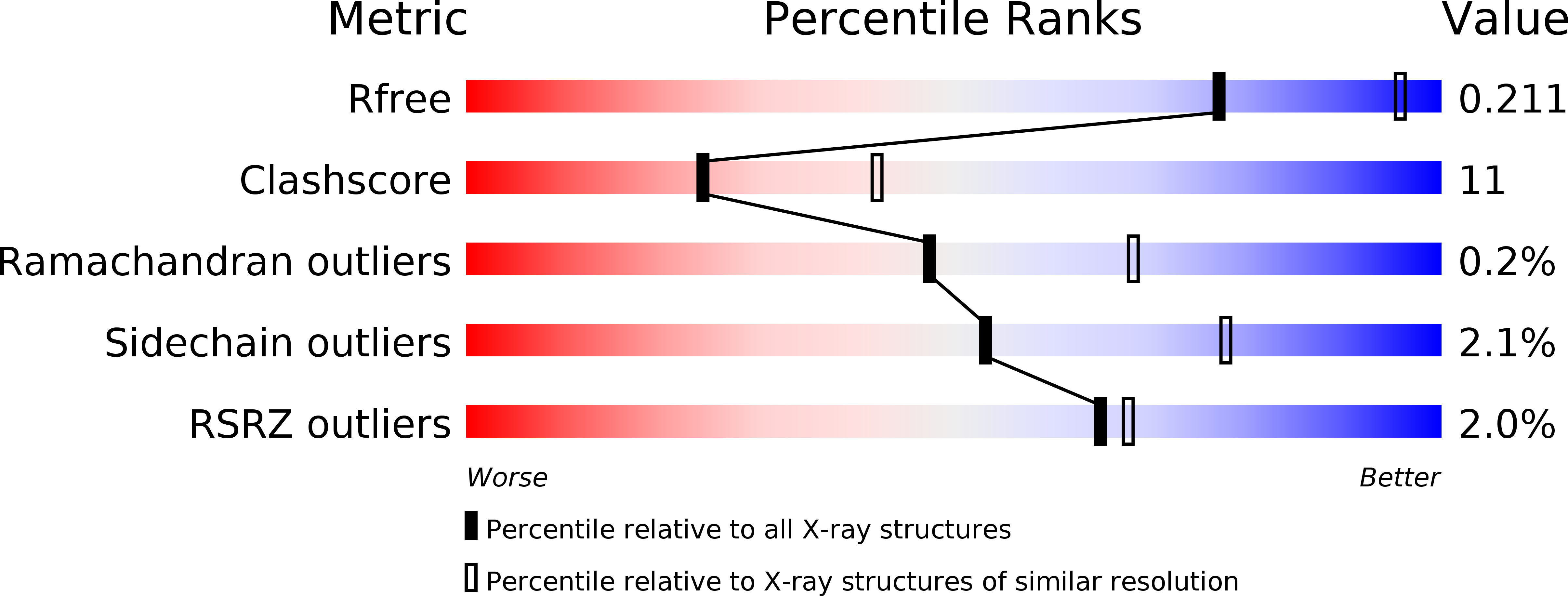
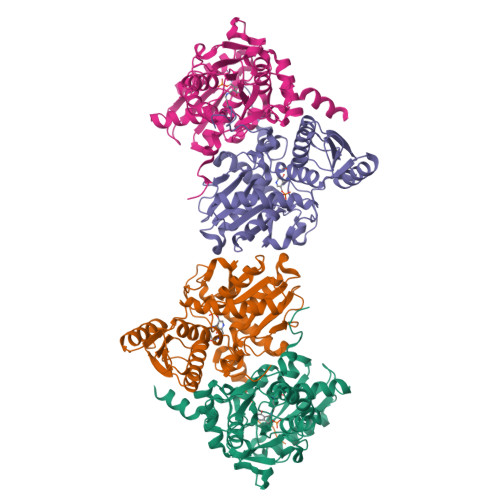
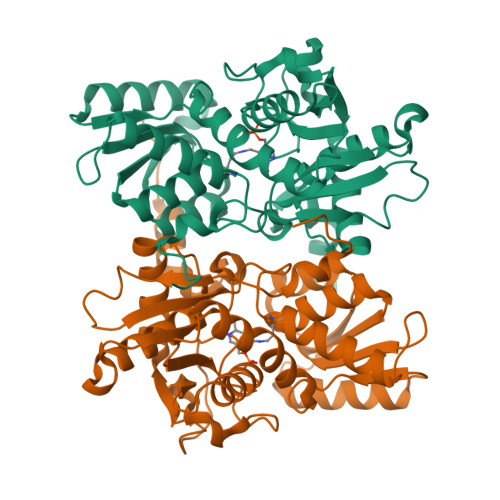
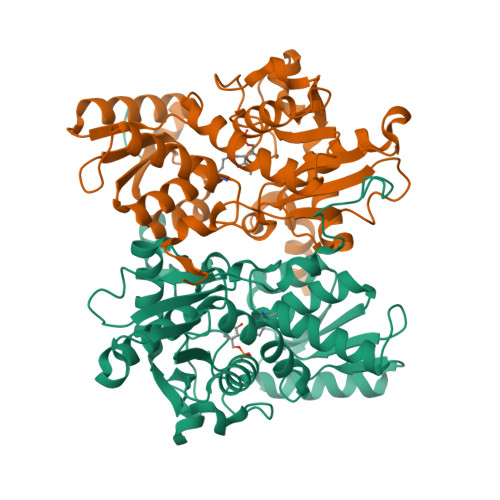
Structure of Soybean beta-Cyanoalanine Synthase and the Molecular Basis for Cyanide Detoxification in Plants.
Yi, H., Juergens, M., Jez, J.M.(2012) Plant Cell 24: 2696-2706
- PubMed: 22739827
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.098954
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3VBE, 3VC3 - PubMed Abstract:
Plants produce cyanide (CN-) during ethylene biosynthesis in the mitochondria and require β-cyanoalanine synthase (CAS) for CN- detoxification. Recent studies show that CAS is a member of the β-substituted alanine synthase (BSAS) family, which also includes the Cys biosynthesis enzyme O-acetylserine sulfhydrylase (OASS), but how the BSAS evolved distinct metabolic functions is not understood. Here we show that soybean (Glycine max) CAS and OASS form α-aminoacrylate reaction intermediates from Cys and O-acetylserine, respectively. To understand the molecular evolution of CAS and OASS in the BSAS enzyme family, the crystal structures of Gm-CAS and the Gm-CAS K95A mutant with a linked pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-Cys molecule in the active site were determined. These structures establish a common fold for the plant BSAS family and reveal a substrate-induced conformational change that encloses the active site for catalysis. Comparison of CAS and OASS identified residues that covary in the PLP binding site. The Gm-OASS T81M, S181M, and T185S mutants altered the ratio of OASS:CAS activity but did not convert substrate preference to that of a CAS. Generation of a triple mutant Gm-OASS successfully switched reaction chemistry to that of a CAS. This study provides new molecular insight into the evolution of diverse enzyme functions across the BSAS family in plants.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology, Washington University, St. Louis, Missouri 63130, USA.