The Structural and Functional Basis of Catalysis Mediated by NAD(P)H:acceptor Oxidoreductase (FerB) of Paracoccus denitrificans.
Sedlacek, V., Klumpler, T., Marek, J., Kucera, I.(2014) PLoS One 9: e96262-e96262
- PubMed: 24817153
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096262
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3U7R - PubMed Abstract:
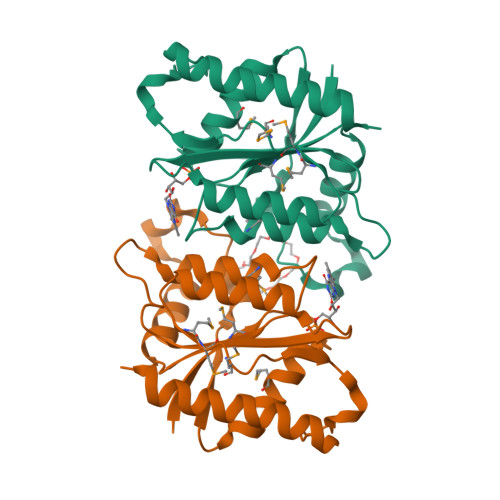
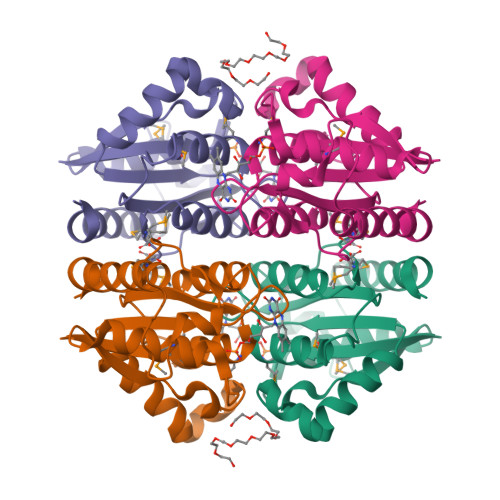
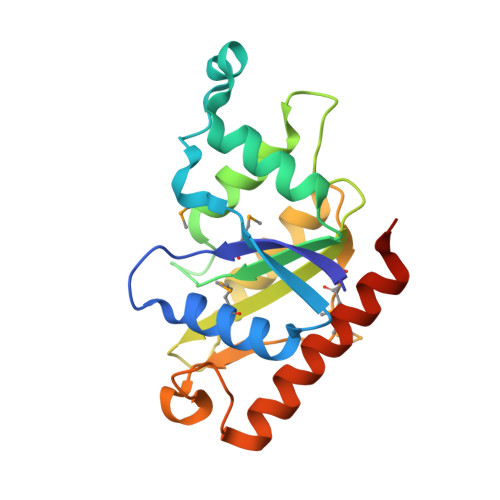
FerB from Paracoccus denitrificans is a soluble cytoplasmic flavoprotein that accepts redox equivalents from NADH or NADPH and transfers them to various acceptors such as quinones, ferric complexes and chromate. The crystal structure and small-angle X-ray scattering measurements in solution reported here reveal a head-to-tail dimer with two flavin mononucleotide groups bound at the opposite sides of the subunit interface. The dimers tend to self-associate to a tetrameric form at higher protein concentrations. Amino acid residues important for the binding of FMN and NADH and for the catalytic activity are identified and verified by site-directed mutagenesis. In particular, we show that Glu77 anchors a conserved water molecule in close proximity to the O2 of FMN, with the probable role of facilitating flavin reduction. Hydride transfer is shown to occur from the 4-pro-S position of NADH to the solvent-accessible si side of the flavin ring. When using deuterated NADH, this process exhibits a kinetic isotope effect of about 6 just as does the NADH-dependent quinone reductase activity of FerB; the first, reductive half-reaction of flavin cofactor is thus rate-limiting. Replacing the bulky Arg95 in the vicinity of the active site with alanine substantially enhances the activity towards external flavins that obeys the standard bi-bi ping-pong reaction mechanism. The new evidence for a cryptic flavin reductase activity of FerB justifies the previous inclusion of this enzyme in the protein family of NADPH-dependent FMN reductases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic.