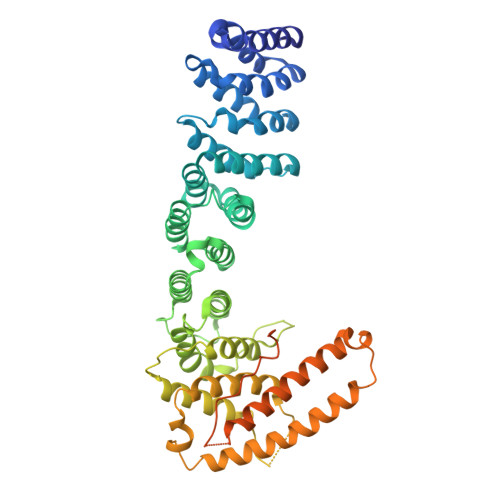
Helical repeat structure of apoptosis inhibitor 5 reveals protein-protein interaction modules.
Han, B.G., Kim, K.H., Lee, S.J., Jeong, K.C., Cho, J.W., Noh, K.H., Kim, T.W., Kim, S.J., Yoon, H.J., Suh, S.W., Lee, S.H., Lee, B.I.(2012) J Biological Chem 287: 10727-10737
- PubMed: 22334682
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.317594
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3U0R, 3V6A - PubMed Abstract:
Apoptosis inhibitor 5 (API5) is an anti-apoptotic protein that is up-regulated in various cancer cells. Here, we present the crystal structure of human API5. API5 exhibits an elongated all α-helical structure. The N-terminal half of API5 is similar to the HEAT repeat and the C-terminal half is similar to the ARM (Armadillo-like) repeat. HEAT and ARM repeats have been implicated in protein-protein interactions, suggesting that the cellular roles of API5 may be to mediate protein-protein interactions. Various components of multiprotein complexes have been identified as API5-interacting protein partners, suggesting that API5 may act as a scaffold for multiprotein complexes. API5 exists as a monomer, and the functionally important heptad leucine repeat does not exhibit the predicted a dimeric leucine zipper. Additionally, Lys-251, which can be acetylated in cells, plays important roles in the inhibition of apoptosis under serum deprivation conditions. The acetylation of this lysine also affects the stability of API5 in cells.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biomolecular Function Research Branch, Division of Convergence Technology, Research Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Gyeonggi 410-769, Korea.