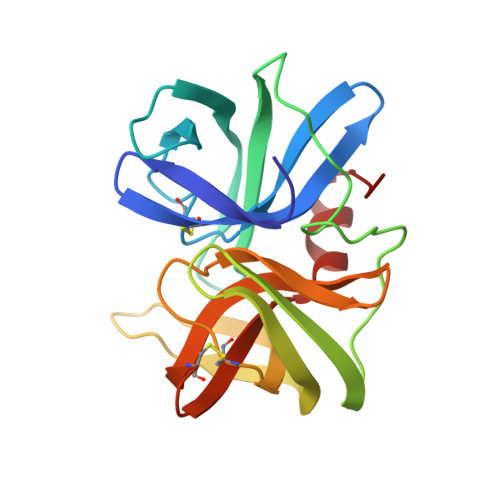
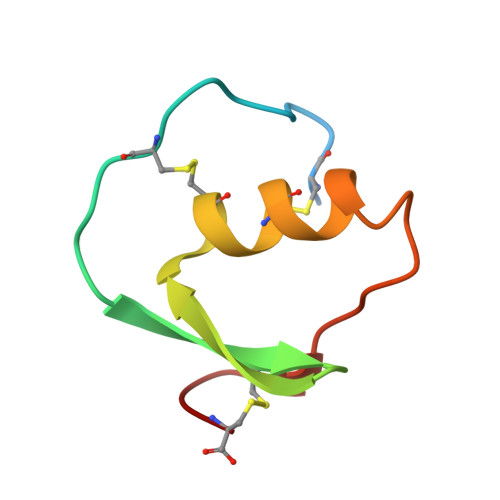
Structure of the complex of Streptomyces griseus protease B and the third domain of the turkey ovomucoid inhibitor at 1.8-A resolution.
Read, R.J., Fujinaga, M., Sielecki, A.R., James, M.N.(1983) Biochemistry 22: 4420-4433
- PubMed: 6414511
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00288a012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3SGB - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of the complex between the serine protease Streptomyces griseus protease B (SGPB) and the third domain of the Kazal-type ovomucoid inhibitor from turkey has been solved at 1.8-A resolution and refined to a conventional R factor of 0.125. As others have reported previously for analogous complexes of proteases and protein inhibitors, the inhibitor binds in a fashion similar to that of a substrate; it is not cleaved, but there is a close approach (2.7 A) of the active site nucleophile Ser-195 O gamma to the carbonyl carbon of the reactive peptide bond of the inhibitor. Contrary to the structural reports regarding the other enzyme-inhibitor complexes, we conclude that there is no evidence for a significant distortion of this peptide bond from planarity. The mechanism of inhibition can be understood in terms of the equilibrium thermodynamic parameters Ka, the enzyme-inhibitor association constant, and Khyd, the equilibrium constant for inhibitor hydrolysis. These thermodynamic parameters can be rationalized in terms of the observed structure.