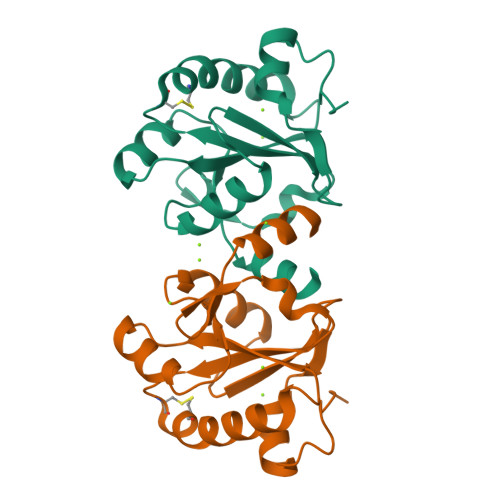
The crystal structures of the tryparedoxin-tryparedoxin peroxidase couple unveil the structural determinants of Leishmania detoxification pathway.
Fiorillo, A., Colotti, G., Boffi, A., Baiocco, P., Ilari, A.(2012) PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6: e1781-e1781
- PubMed: 22928053
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0001781
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3S9F, 3TUE - PubMed Abstract:
Leishmaniasis is a neglected disease caused by Leishmania, an intracellular protozoan parasite which possesses a unique thiol metabolism based on trypanothione. Trypanothione is used as a source of electrons by the tryparedoxin/tryparedoxin peroxidase system (TXN/TXNPx) to reduce the hydroperoxides produced by macrophages during infection. This detoxification pathway is not only unique to the parasite but is also essential for its survival; therefore, it constitutes a most attractive drug target. Several forms of TXNPx, with very high sequence identity to one another, have been found in Leishmania strains, one of which has been used as a component of a potential anti-leishmanial polyprotein vaccine. The structures of cytosolic TXN and TXNPx from L. major (LmTXN and LmTXNPx) offer a unique opportunity to study peroxide reduction in Leishmania parasites at a molecular level, and may provide new tools for multienzyme inhibition-based drug discovery. Structural analyses bring out key structural features to elucidate LmTXN and LmTXNPx function. LmTXN displays an unusual N-terminal α-helix which allows the formation of a stable domain-swapped dimer. In LmTXNPx, crystallized in reducing condition, both the locally unfolded (LU) and fully folded (FF) conformations, typical of the oxidized and reduced protein respectively, are populated. The structural analysis presented here points to a high flexibility of the loop that includes the peroxidatic cysteine which facilitates Cys52 to form an inter-chain disulfide bond with the resolving cysteine (Cys173), thereby preventing over-oxidation which would inactivate the enzyme. Analysis of the electrostatic surface potentials of both LmTXN and LmTXNPx unveils the structural elements at the basis of functionally relevant interaction between the two proteins. Finally, the structural analysis of TXNPx allows us to identify the position of the epitopes that make the protein antigenic and therefore potentially suitable to be used in an anti-leishmanial polyprotein vaccine.
Organizational Affiliation:
Dipartimento di Scienze Biochimiche, University Sapienza, Rome, Italy.