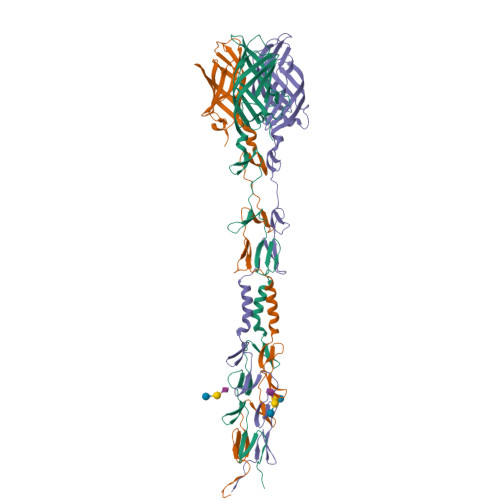
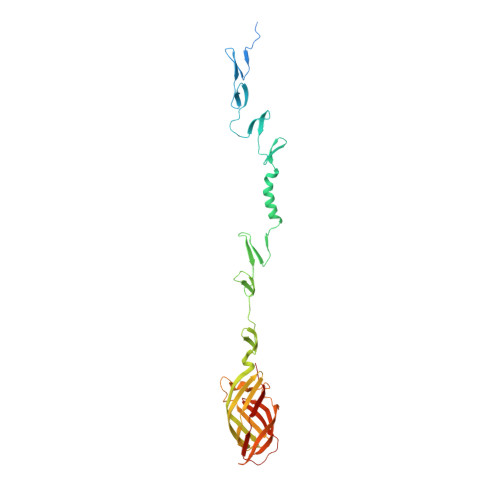
Crystal structure of reovirus attachment protein sigma1 in complex with sialylated oligosaccharides
Reiter, D.M., Frierson, J.M., Halvorson, E.E., Kobayashi, T., Dermody, T.S., Stehle, T.(2011) PLoS Pathog 7: e1002166-e1002166
- PubMed: 21829363
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002166
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3S6X, 3S6Y, 3S6Z - PubMed Abstract:
Many viruses attach to target cells by binding to cell-surface glycans. To gain a better understanding of strategies used by viruses to engage carbohydrate receptors, we determined the crystal structures of reovirus attachment protein σ1 in complex with α-2,3-sialyllactose, α-2,6-sialyllactose, and α-2,8-di-siallylactose. All three oligosaccharides terminate in sialic acid, which serves as a receptor for the reovirus serotype studied here. The overall structure of σ1 resembles an elongated, filamentous trimer. It contains a globular head featuring a compact β-barrel, and a fibrous extension formed by seven repeating units of a triple β-spiral that is interrupted near its midpoint by a short α-helical coiled coil. The carbohydrate-binding site is located between β-spiral repeats two and three, distal from the head. In all three complexes, the terminal sialic acid forms almost all of the contacts with σ1 in an identical manner, while the remaining components of the oligosaccharides make little or no contacts. We used this structural information to guide mutagenesis studies to identify residues in σ1 that functionally engage sialic acid by assessing hemagglutination capacity and growth in murine erythroleukemia cells, which require sialic acid binding for productive infection. Our studies using σ1 mutant viruses reveal that residues 198, 202, 203, 204, and 205 are required for functional binding to sialic acid by reovirus. These findings provide insight into mechanisms of reovirus attachment to cell-surface glycans and contribute to an understanding of carbohydrate binding by viruses. They also establish a filamentous, trimeric carbohydrate-binding module that could potentially be used to endow other trimeric proteins with carbohydrate-binding properties.
Organizational Affiliation:
Interfaculty Institute of Biochemistry, University of Tuebingen, Tuebingen, Germany.