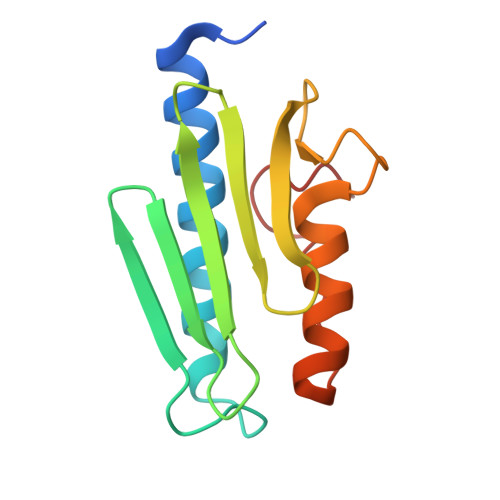
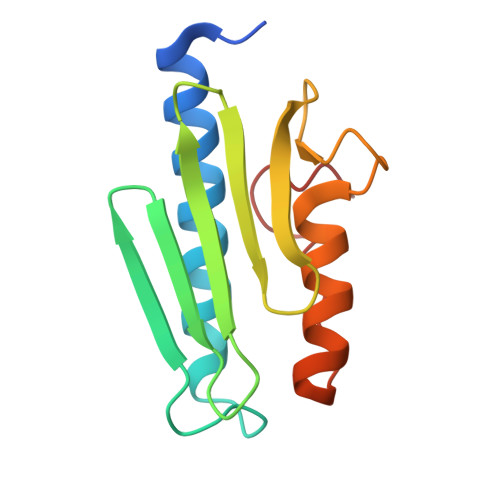
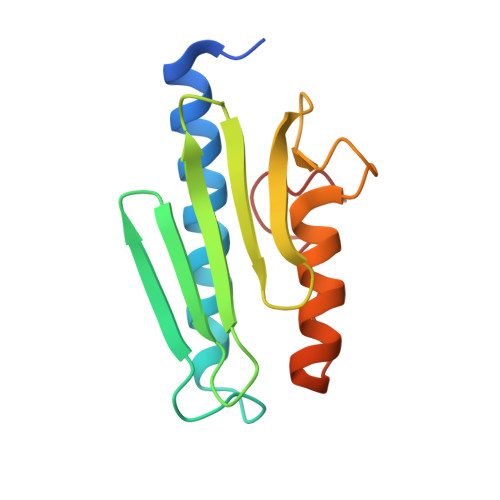
Friedreich's Ataxia Variants I154F and W155R Diminish Frataxin-Based Activation of the Iron-Sulfur Cluster Assembly Complex.
Tsai, C.L., Bridwell-Rabb, J., Barondeau, D.P.(2011) Biochemistry 50: 6478-6487
- PubMed: 21671584
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi200666h
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3S4M, 3S5D, 3S5E, 3S5F - PubMed Abstract:
Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that has been linked to defects in the protein frataxin (Fxn). Most FRDA patients have a GAA expansion in the first intron of their Fxn gene that decreases protein expression. Some FRDA patients have a GAA expansion on one allele and a missense mutation on the other allele. Few functional details are known for the ∼15 different missense mutations identified in FRDA patients. Here in vitro evidence is presented that indicates the FRDA I154F and W155R variants bind more weakly to the complex of Nfs1, Isd11, and Isu2 and thereby are defective in forming the four-component SDUF complex that constitutes the core of the Fe-S cluster assembly machine. The binding affinities follow the trend Fxn ∼ I154F > W155F > W155A ∼ W155R. The Fxn variants also have diminished ability to function as part of the SDUF complex to stimulate the cysteine desulfurase reaction and facilitate Fe-S cluster assembly. Four crystal structures, including the first for a FRDA variant, reveal specific rearrangements associated with the loss of function and lead to a model for Fxn-based activation of the Fe-S cluster assembly complex. Importantly, the weaker binding and lower activity for FRDA variants correlate with the severity of disease progression. Together, these results suggest that Fxn facilitates sulfur transfer from Nfs1 to Isu2 and that these in vitro assays are sensitive and appropriate for deciphering functional defects and mechanistic details for human Fe-S cluster biosynthesis.
Organizational Affiliation:
barondeau@tamu.edu