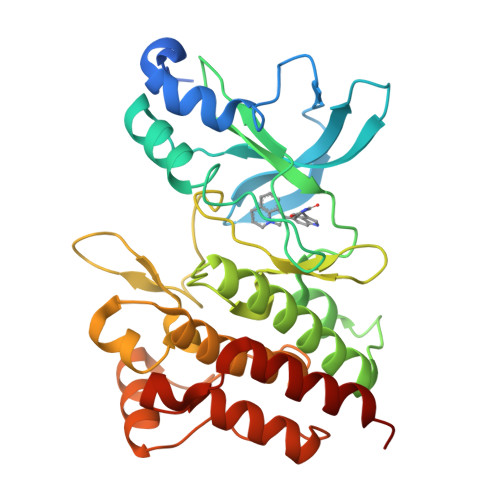
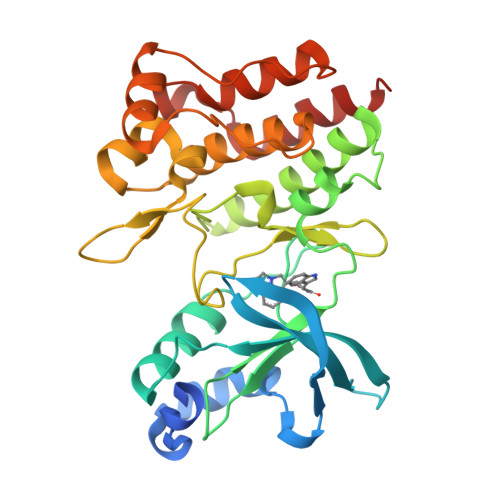
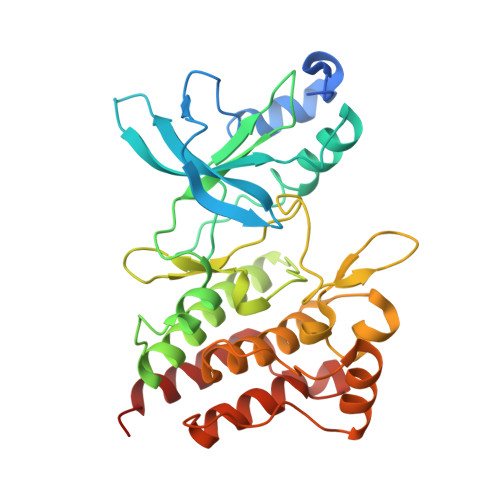
Discovery of a novel mode of protein kinase inhibition characterized by the mechanism of inhibition of human mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-Met) protein autophosphorylation by ARQ 197.
Eathiraj, S., Palma, R., Volckova, E., Hirschi, M., France, D.S., Ashwell, M.A., Chan, T.C.(2011) J Biological Chem 286: 20666-20676
- PubMed: 21454604
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.213801
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3RHK - PubMed Abstract:
A number of human malignancies exhibit sustained stimulation, mutation, or gene amplification of the receptor tyrosine kinase human mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-Met). ARQ 197 is a clinically advanced, selective, orally bioavailable, and well tolerated c-Met inhibitor, currently in Phase 3 clinical testing in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Herein, we describe the molecular and structural basis by which ARQ 197 selectively targets c-Met. Through our analysis we reveal a previously undisclosed, novel inhibitory mechanism that utilizes distinct regulatory elements of the c-Met kinase. The structure of ARQ 197 in complex with the c-Met kinase domain shows that the inhibitor binds a conformation that is distinct from published kinase structures. ARQ 197 inhibits c-Met autophosphorylation and is highly selective for the inactive or unphosphorylated form of c-Met. Through our analysis of the interplay between the regulatory and catalytic residues of c-Met, and by comparison between the autoinhibited canonical conformation of c-Met bound by ARQ 197 to previously described kinase domains of type III receptor tyrosine kinases, we believe this to be the basis of a powerful new in silico approach for the design of similar inhibitors for other protein kinases of therapeutic interest.
Organizational Affiliation:
ArQule, Inc, Woburn, Massachusetts 01801, USA.