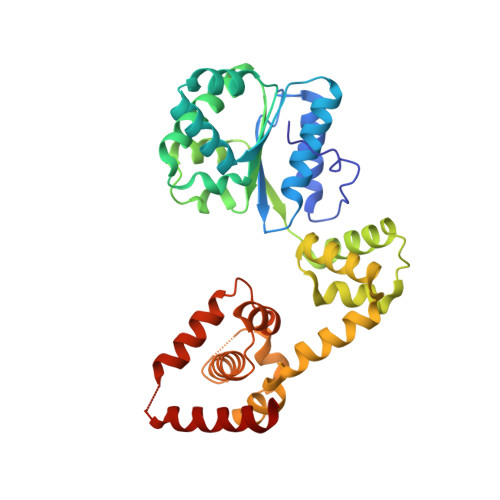
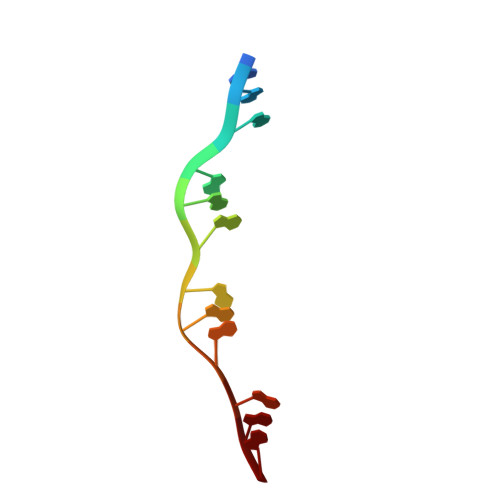
DNA stretching by bacterial initiators promotes replication origin opening.
Duderstadt, K.E., Chuang, K., Berger, J.M.(2011) Nature 478: 209-213
- PubMed: 21964332
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10455
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3R8F - PubMed Abstract:
Many replication initiators form higher-order oligomers that process host replication origins to promote replisome formation. In addition to dedicated duplex-DNA-binding domains, cellular initiators possess AAA+ (ATPases associated with various cellular activities) elements that drive functions ranging from protein assembly to origin recognition. In bacteria, the AAA+ domain of the initiator DnaA has been proposed to assist in single-stranded DNA formation during origin melting. Here we show crystallographically and in solution that the ATP-dependent assembly of Aquifex aeolicus DnaA into a spiral oligomer creates a continuous surface that allows successive AAA+ domains to bind and extend single-stranded DNA segments. The mechanism of binding is unexpectedly similar to that of RecA, a homologous recombination factor, but it differs in that DnaA promotes a nucleic acid conformation that prevents pairing of a complementary strand. These findings, combined with strand-displacement assays, indicate that DnaA opens replication origins by a direct ATP-dependent stretching mechanism. Comparative studies reveal notable commonalities between the approach used by DnaA to engage DNA substrates and other, nucleic-acid-dependent, AAA+ systems.
- Biophysics Graduate Group, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, California 94720, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: