Structure, Activity, and Substrate Selectivity of the Orf6 Thioesterase from Photobacterium profundum.
Rodriguez-Guilbe, M., Oyola-Robles, D., Schreiter, E.R., Baerga-Ortiz, A.(2013) J Biological Chem 288: 10841-10848
- PubMed: 23430744
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.446765
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3R87, 4I45 - PubMed Abstract:
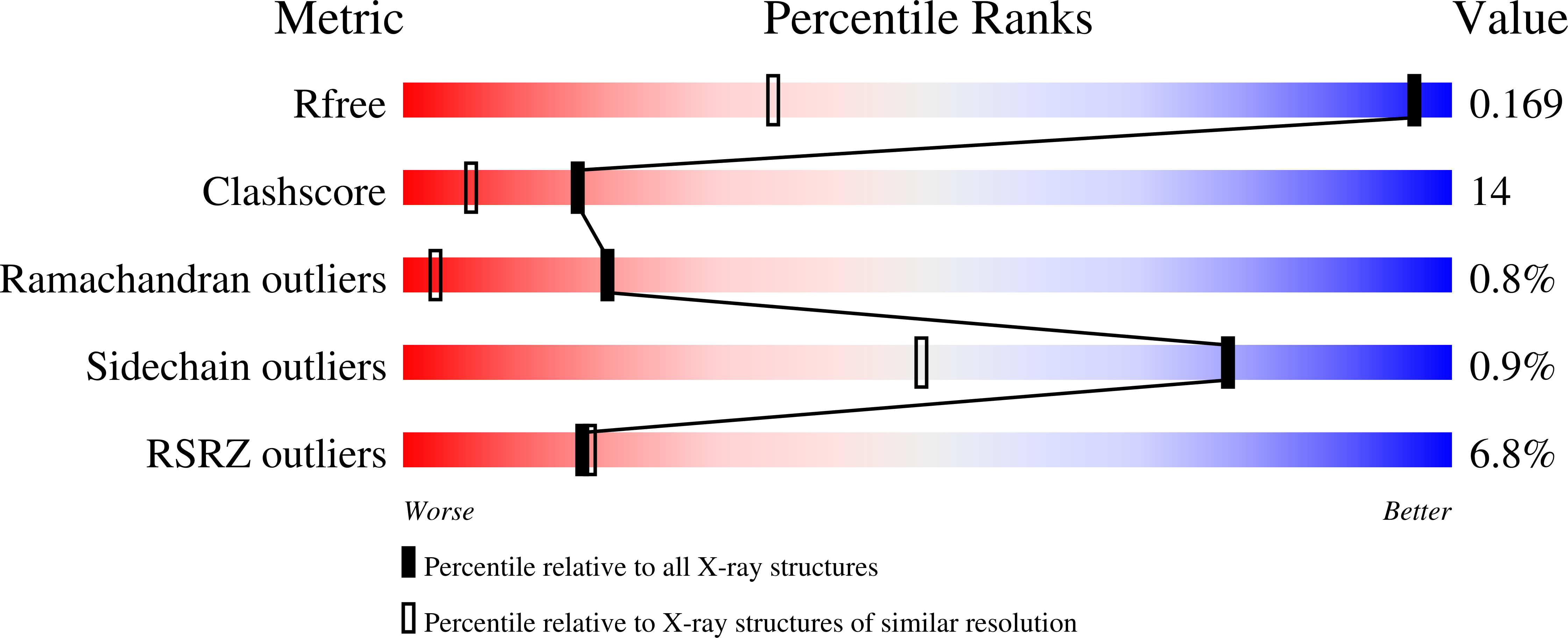
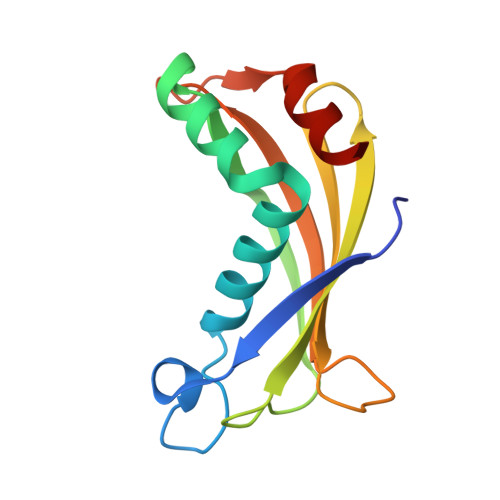
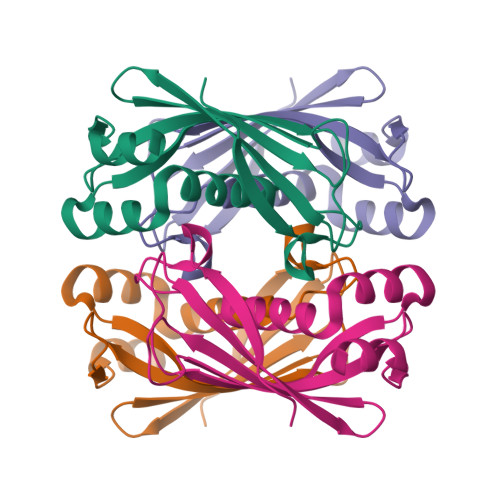
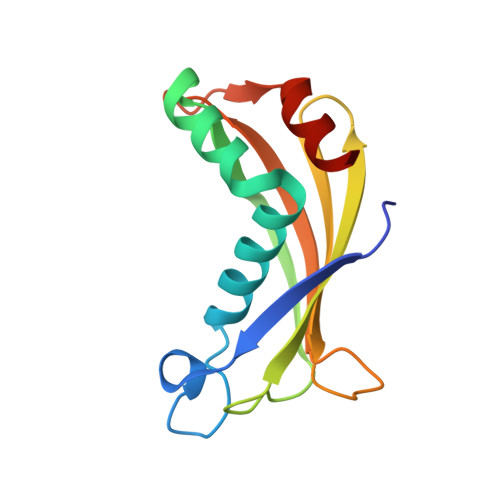
Thioesterase activity is typically required for the release of products from polyketide synthase enzymes, but no such enzyme has been characterized in deep-sea bacteria associated with the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids. In this work, we have expressed and purified the Orf6 thioesterase from Photobacterium profundum. Enzyme assays revealed that Orf6 has a higher specific activity toward long-chain fatty acyl-CoA substrates (palmitoyl-CoA and eicosapentaenoyl-CoA) than toward short-chain or aromatic acyl-CoA substrates. We determined a high resolution (1.05 Å) structure of Orf6 that reveals a hotdog hydrolase fold arranged as a dimer of dimers. The putative active site of this structure is occupied by additional electron density not accounted for by the protein sequence, consistent with the presence of an elongated compound. A second crystal structure (1.40 Å) was obtained from a crystal that was grown in the presence of Mg(2+), which reveals the presence of a binding site for divalent cations at a crystal contact. The Mg(2+)-bound structure shows localized conformational changes (root mean square deviation of 1.63 Å), and its active site is unoccupied, suggesting a mechanism to open the active site for substrate entry or product release. These findings reveal a new thioesterase enzyme with a preference for long-chain CoA substrates in a deep-sea bacterium whose potential range of applications includes bioremediation and the production of biofuels.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Puerto Rico School of Medicine, San Juan, Puerto Rico.