Structural Basis for Differential Insertion Kinetics of dNMPs Opposite a Difluorotoluene Nucleotide Residue.
Xia, S., Eom, S.H., Konigsberg, W.H., Wang, J.(2012) Biochemistry 51: 1476-1485
- PubMed: 22304682
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi2016487
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3QEI, 3QER, 3QES - PubMed Abstract:
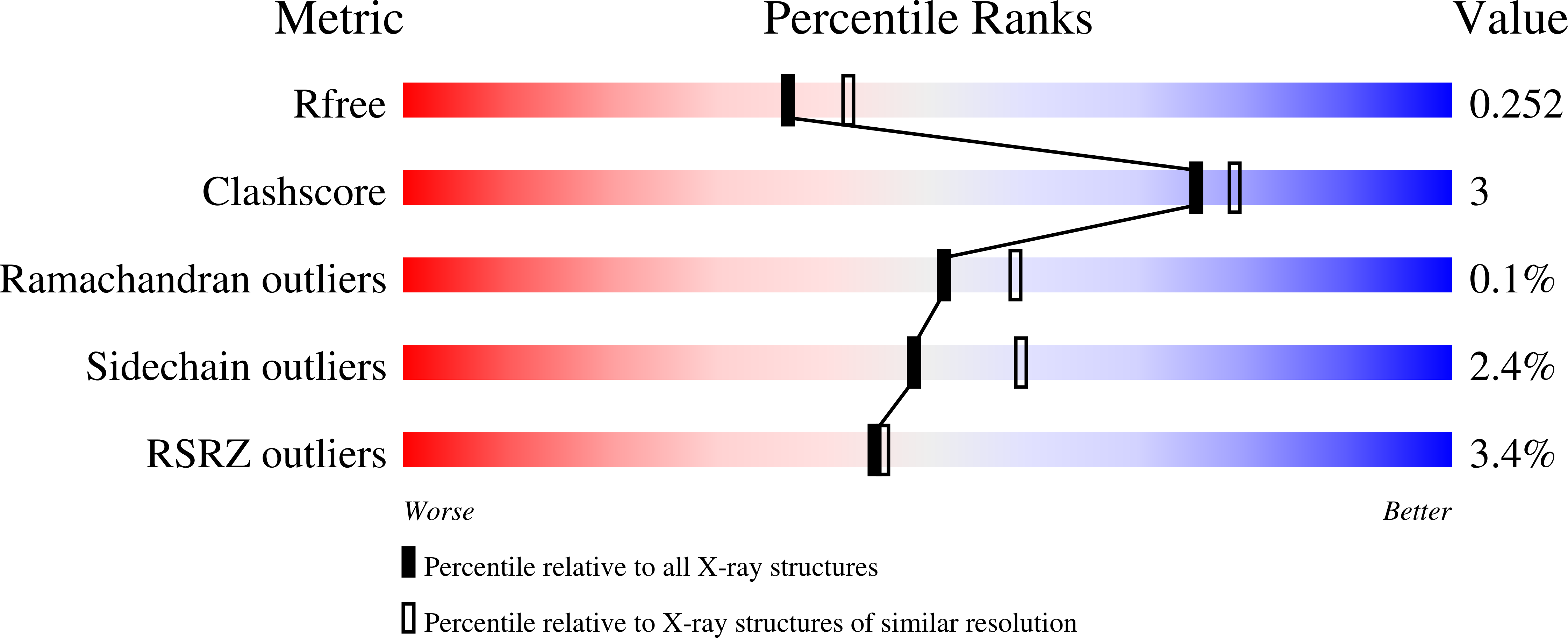
We have recently challenged the widely held view that 2,4-difluorotoluene (dF) is a nonpolar isosteric analogue of the nucleotide dT, incapable of forming hydrogen bonds (HBs). To gain a further understanding for the kinetic preference that favors dAMP insertion opposite a templating dF, a result that mirrors the base selectivity that favors dAMP insertion opposite dT by RB69 DNA polymerase (RB69pol), we determined presteady-state kinetic parameters for incorporation of four dNMPs opposite dF by RB69pol and solved the structures of corresponding ternary complexes. We observed that both the F2 and F4 substituent of dF in these structures serve as HB acceptors forming HBs either directly with dTTP and dGTP or indirectly with dATP and dCTP via ordered water molecules. We have defined the shape and chemical features of each dF/dNTP pair in the RB69pol active site without the corresponding phosphodiester-linkage constraints of dF/dNs when they are embedded in isolated DNA duplexes. These features can explain the kinetic preferences exhibited by the templating dF when the nucleotide incorporation is catalyzed by wild type RB69pol or its mutants. We further show that the shapes of the dNTP/dF nascent base pair differ markedly from the corresponding dNTP/dT in the pol active site and that these differences have a profound effect on their incorporation efficiencies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8114, United States.