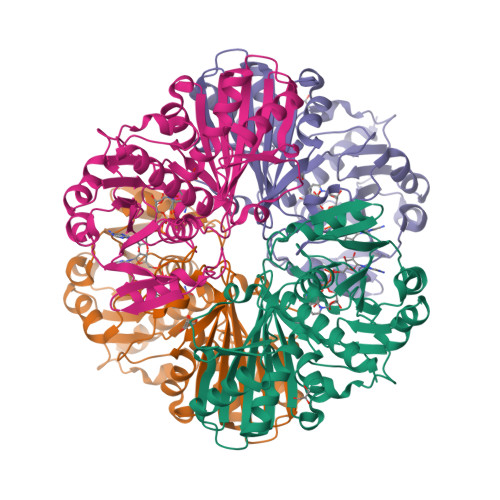
Structure and kinetic characterization of human sperm-specific glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, GAPDS.
Chaikuad, A., Shafqat, N., Al-Mokhtar, R., Cameron, G., Clarke, A.R., Brady, R.L., Oppermann, U., Frayne, J., Yue, W.W.(2011) Biochem J 435: 401-409
- PubMed: 21269272
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20101442
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3H9E, 3PFW - PubMed Abstract:
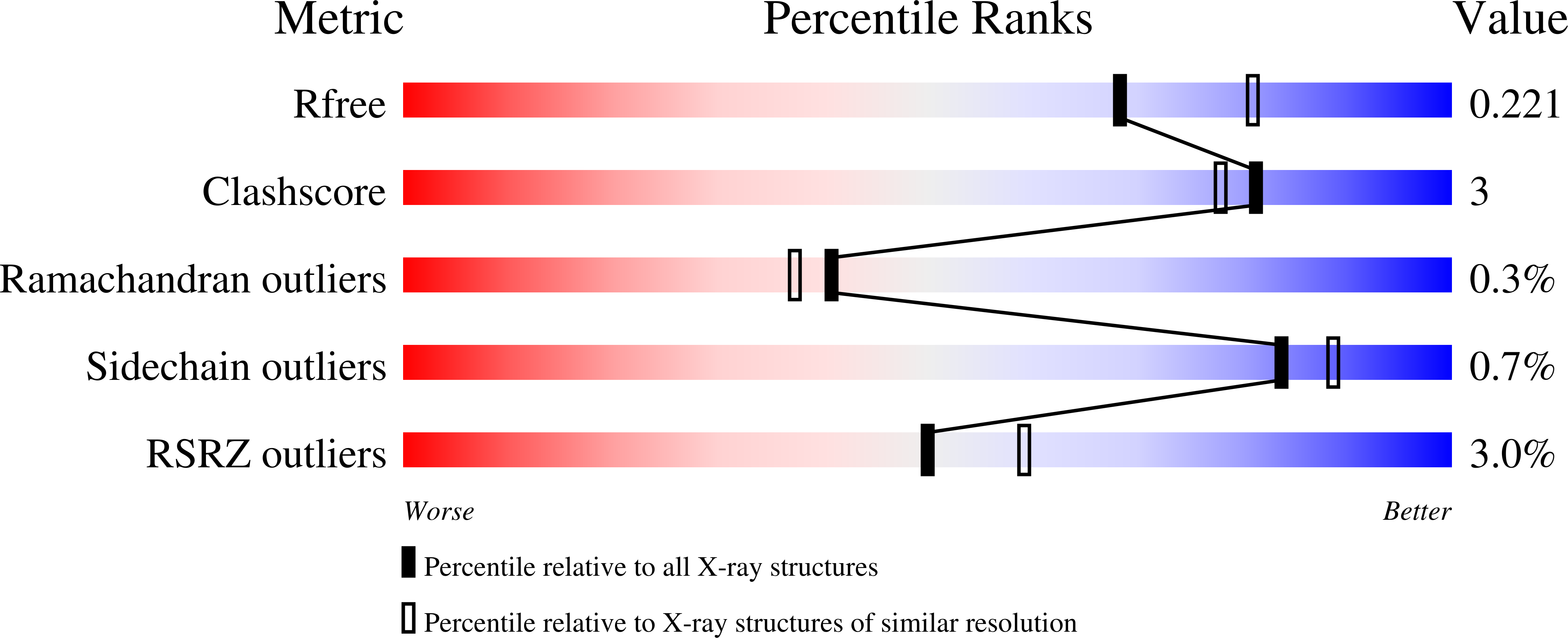
hGAPDS (human sperm-specific glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) is a glycolytic enzyme essential for the survival of spermatozoa, and constitutes a potential target for non-hormonal contraception. However, enzyme characterization of GAPDS has been hampered by the difficulty in producing soluble recombinant protein. In the present study, we have overexpressed in Escherichia coli a highly soluble form of hGAPDS truncated at the N-terminus (hGAPDSΔN), and crystallized the homotetrameric enzyme in two ligand complexes. The hGAPDSΔN-NAD+-phosphate structure maps the two anion-recognition sites within the catalytic pocket that correspond to the conserved Ps site and the newly recognized Pi site identified in other organisms. The hGAPDSΔN-NAD+-glycerol structure shows serendipitous binding of glycerol at the Ps and new Pi sites, demonstrating the propensity of these anion-recognition sites to bind non-physiologically relevant ligands. A comparison of kinetic profiles between hGAPDSΔN and its somatic equivalent reveals a 3-fold increase in catalytic efficiency for hGAPDSΔN. This may be attributable to subtle amino acid substitutions peripheral to the active centre that influence the charge properties and protonation states of catalytic residues. Our data therefore elucidate structural and kinetic features of hGAPDS that might provide insightful information towards inhibitor development.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Genomics Consortium, University of Oxford, Oxford OX3 7DQ, UK.