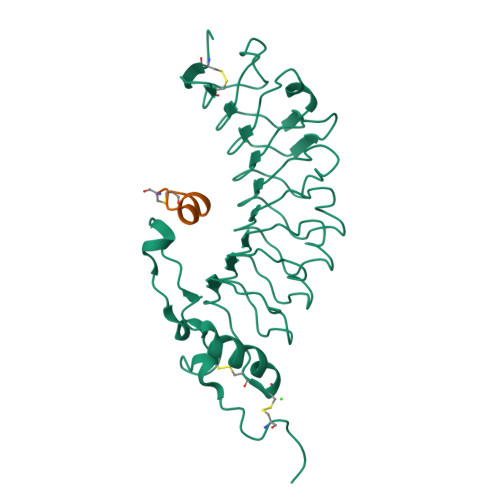
Glycoprotein Ibalpha inhibitor complex structure reveals a combined steric and allosteric mechanism of von Willebrand factor antagonism.
McEwan, P.A., Andrews, R.K., Emsley, J.(2009) Blood 114: 4883-4885
- PubMed: 19726719
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-05-224170
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
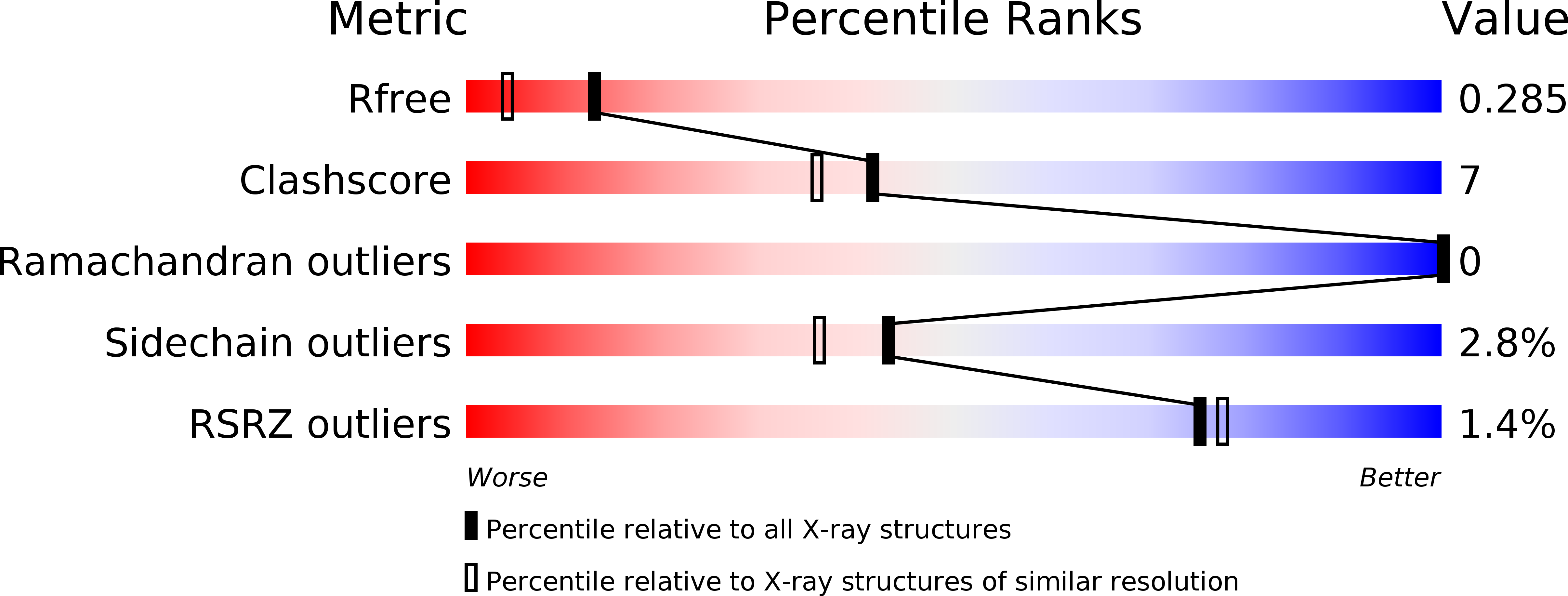
3P72 - PubMed Abstract:
Platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha (GpIbalpha) interactions with von Willebrand factor (VWF) are a critical early event in platelet adhesion, which contributes to hemostasis and thrombosis. Here we report the structure of a complex between GpIbalpha and a potent peptide inhibitor. The cyclic peptide (CTERMALHNLC) was isolated from a cysteine-constrained phage display library, and in the complex this forms one and a half turns of an amphipathic alpha-helix, the curvature of which facilitates contacts with the curved concave face of the GpIbalpha leucine-rich repeats. The peptide has only limited overlap with the VWF binding site. It effectively inhibits by stabilizing an alternative alpha-helical conformation of a regulatory loop that forms an extended beta-hairpin upon VWF binding. The structure defines a previously unrecognized binding site within GpIbalpha and represents a clear strategy for developing antiplatelet agents targeting the GpIbalpha-VWF interaction allosterically.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre for Biomolecular Sciences, School of Pharmacy, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom.