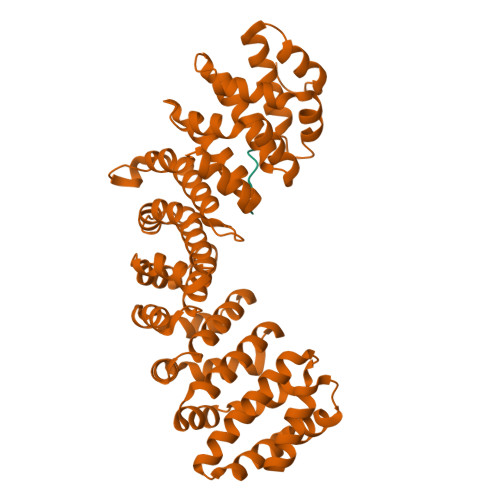
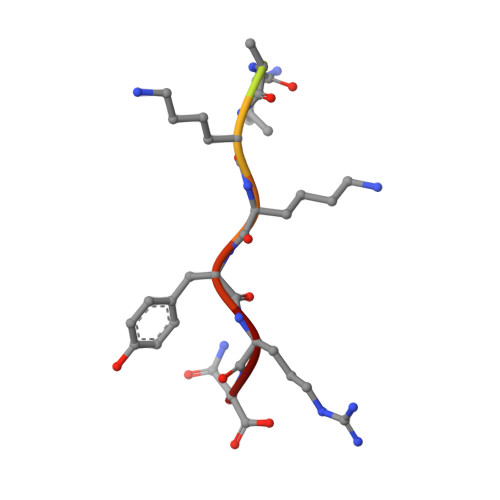
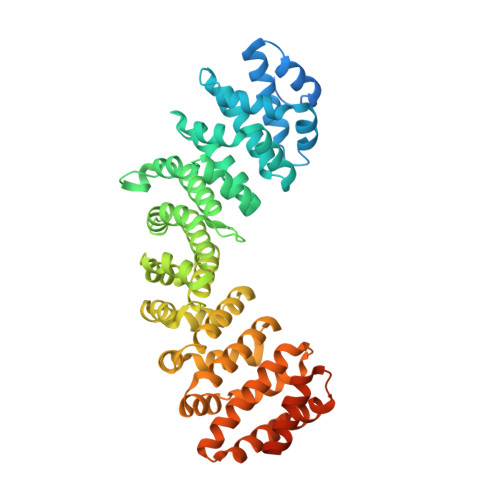
Crystal structure of importin-alpha bound to a peptide bearing the nuclear localisation signal from chloride intracellular channel protein 4
Mynott, A.V., Harrop, S.J., Brown, L.J., Breit, S.N., Kobe, B., Curmi, P.M.G.(2011) FEBS J 278: 1662-1675
- PubMed: 21388519
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08086.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3OQS - PubMed Abstract:
It has been reported that a human chloride intracellular channel (CLIC) protein, CLIC4, translocates to the nucleus in response to cellular stress, facilitated by a putative CLIC4 nuclear localization signal (NLS). The CLIC4 NLS adopts an α-helical structure in the native CLIC4 fold. It is proposed that CLIC4 is transported to the nucleus via the classical nuclear import pathway after binding the import receptor, importin-α. In this study, we have determined the X-ray crystal structure of a truncated form of importin-α lacking the importin-β binding domain, bound to a CLIC4 NLS peptide. The NLS peptide binds to the major binding site in an extended conformation similar to that observed for the classical simian virus 40 large T-antigen NLS. A Tyr residue within the CLIC4 NLS makes surprisingly favourable interactions by forming side-chain hydrogen bonds to the importin-α backbone. This structural evidence supports the hypothesis that CLIC4 translocation to the nucleus is governed by the importin-α nuclear import pathway, provided that CLIC4 can undergo a conformational rearrangement that exposes the NLS in an extended conformation.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Physics, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW, Australia.