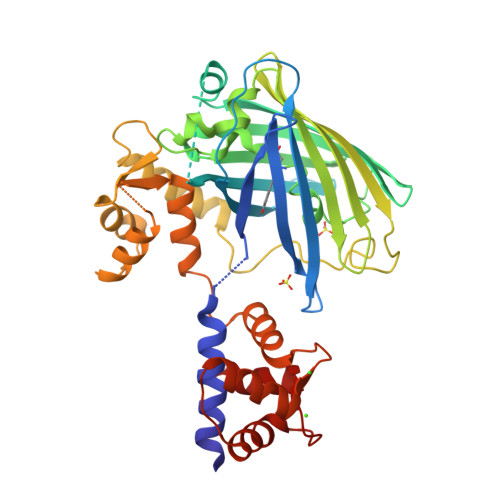
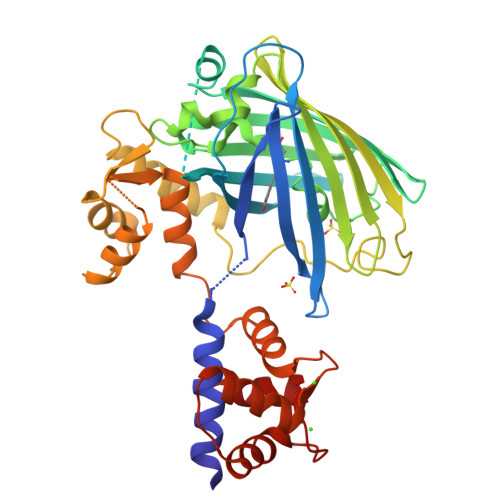
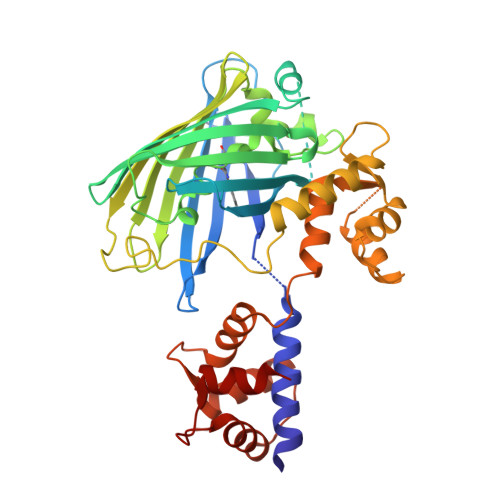
The structure of Ca2+ sensor Case16 reveals the mechanism of reaction to low Ca2+ concentrations
Leder, L., Stark, W., Freuler, F., Marsh, M., Meyerhofer, M., Stettler, T., Mayr, L.M., Britanova, O.V., Strukova, L.A., Chudakov, D.M., Souslova, E.A.(2010) Sensors (Basel) 10: 8143-8160
- PubMed: 22163646
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/s100908143
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3O77, 3O78 - PubMed Abstract:
Here we report the first crystal structure of a high-contrast genetically encoded circularly permuted green fluorescent protein (cpGFP)-based Ca(2+) sensor, Case16, in the presence of a low Ca(2+) concentration. The structure reveals the positioning of the chromophore within Case16 at the first stage of the Ca(2+)-dependent response when only two out of four Ca(2+)-binding pockets of calmodulin (CaM) are occupied with Ca(2+) ions. In such a "half Ca(2+)-bound state", Case16 is characterized by an incomplete interaction between its CaM-/M13-domains. We also report the crystal structure of the related Ca(2+) sensor Case12 at saturating Ca(2+) concentration. Based on this structure, we postulate that cpGFP-based Ca(2+) sensors can form non-functional homodimers where the CaM-domain of one sensor molecule binds symmetrically to the M13-peptide of the partner sensor molecule. Case12 and Case16 behavior upon addition of high concentrations of free CaM or M13-peptide reveals that the latter effectively blocks the fluorescent response of the sensor. We speculate that the demonstrated intermolecular interaction with endogenous substrates and homodimerization can impede proper functioning of this type of Ca(2+) sensors in living cells.
Organizational Affiliation:
Novartis Pharma AG, NIBR/CPC/LFP, Lichtstrasse 35, CH-4002 Basel, Switzerland. lukas.leder@novartis.com